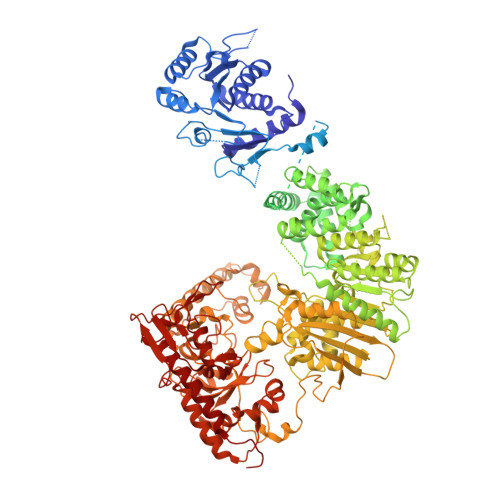
Structural insights into DNA sequence recognition by Type ISP restriction-modification enzymes
Kulkarni, M., Nirwan, N., van Aelst, K., Szczelkun, M.D., Saikrishnan, K.(2016) Nucleic Acids Res 44: 4396-4408
- PubMed: 26975655
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw154
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5FFJ - PubMed Abstract:
Engineering restriction enzymes with new sequence specificity has been an unaccomplished challenge, presumably because of the complexity of target recognition. Here we report detailed analyses of target recognition by Type ISP restriction-modification enzymes. We determined the structure of the Type ISP enzyme LlaGI bound to its target and compared it with the previously reported structure of a close homologue that binds to a distinct target, LlaBIII. The comparison revealed that, although the two enzymes use almost a similar set of structural elements for target recognition, the residues that read the bases vary. Change in specificity resulted not only from appropriate substitution of amino acids that contacted the bases but also from new contacts made by positionally distinct residues directly or through a water bridge. Sequence analyses of 552 Type ISP enzymes showed that the structural elements involved in target recognition of LlaGI and LlaBIII were structurally well-conserved but sequentially less-conserved. In addition, the residue positions within these structural elements were under strong evolutionary constraint, highlighting the functional importance of these regions. The comparative study helped decipher a partial consensus code for target recognition by Type ISP enzymes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biology, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune 411008, India.