An aminoquinazoline inhibitor of the essential bacterial cell wall synthetic enzyme GlmU has a unique non-protein-kinase-like binding mode.
Larsen, N.A., Nash, T.J., Morningstar, M., Shapiro, A.B., Joubran, C., Blackett, C.J., Patten, A.D., Boriack-Sjodin, P.A., Doig, P.(2012) Biochem J 446: 405-413
- PubMed: 22721802
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20120596
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
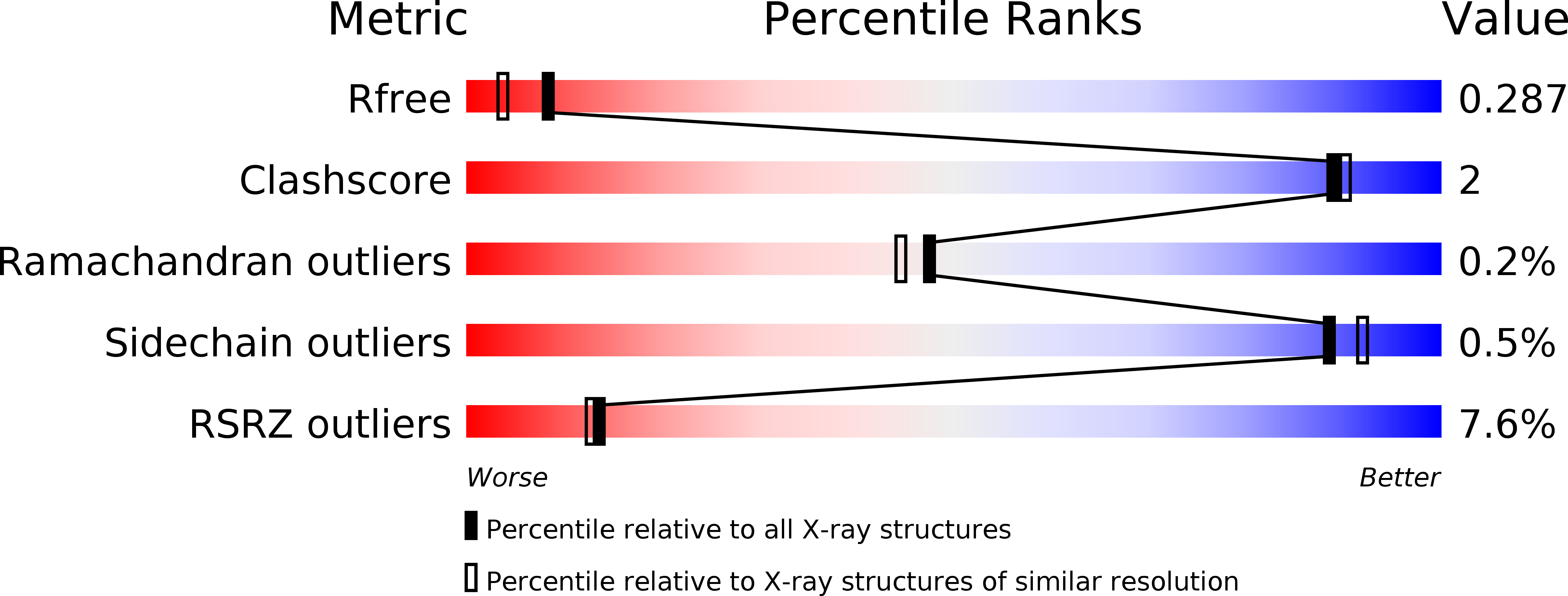
4E1K - PubMed Abstract:
GlmU is a bifunctional enzyme with acetyltransferase and uridyltransferase activities, and is essential for the biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Inhibition results in a loss of cell viability. GlmU is therefore considered a potential target for novel antibacterial agents. A HTS (high-throughput screen) identified a series of aminoquinazolines with submicromolar potency against the uridyltransferase reaction. Biochemical and biophysical characterization showed competition with UTP binding. We determined the crystal structure of a representative aminoquinazoline bound to the Haemophilus influenzae isoenzyme at a resolution of 2.0 Å. The inhibitor occupies part of the UTP site, skirts the outer perimeter of the GlcNAc1-P (N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate) pocket and anchors a hydrophobic moiety into a lipophilic pocket. Our SAR (structure-activity relationship) analysis shows that all of these interactions are essential for inhibitory activity in this series. The crystal structure suggests that the compound would block binding of UTP and lock GlmU in an apo-enzyme-like conformation, thus interfering with its enzymatic activity. Our lead generation effort provides ample scope for further optimization of these compounds for antibacterial drug discovery.
Organizational Affiliation:
Discovery Sciences Unit, AstraZeneca R&D Boston, Waltham, MA 02451, USA.