The Structure of Serratia Marcescens Lip, a Membrane-Bound Component of the Type Vi Secretion System
Rao, V.A., Shepherd, S.M., English, G., Coulthurst, S.J., Hunter, W.N.(2011) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67: 1065
- PubMed: 22120744
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444911046300
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4A1R - PubMed Abstract:
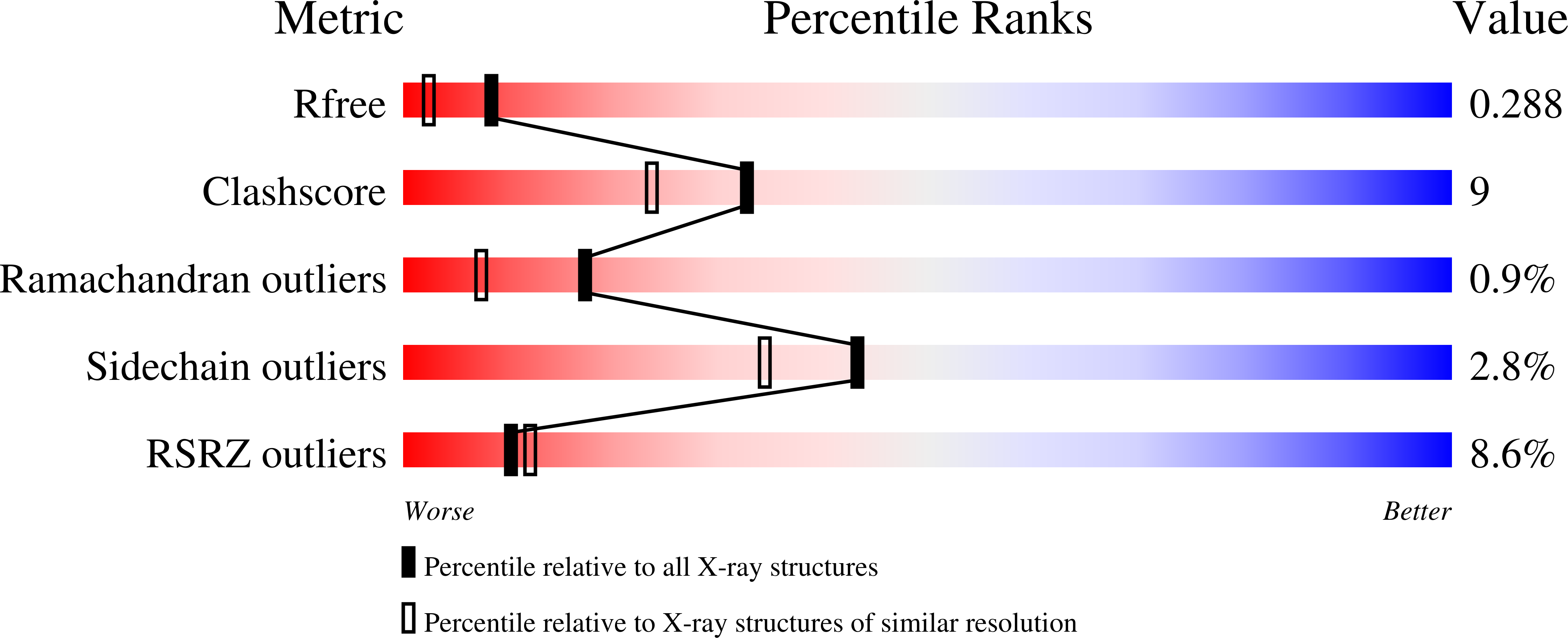
Lip is a membrane-bound lipoprotein and a core component of the type VI secretion system found in Gram-negative bacteria. The structure of a Lip construct (residues 29-176) from Serratia marcescens (SmLip) has been determined at 1.92 Å resolution. Experimental phases were derived using a single-wavelength anomalous dispersion approach on a sample cocrystallized with iodide. The membrane localization of the native protein was confirmed. The structure is that of the globular domain lacking only the lipoprotein signal peptide and the lipidated N-terminus of the mature protein. The protein fold is dominated by an eight-stranded β-sandwich and identifies SmLip as a new member of the transthyretin family of proteins. Transthyretin and the only other member of the family fold, 5-hydroxyisourate hydrolase, form homotetramers important for their function. The asymmetric unit of SmLip is a tetramer with 222 symmetry, but the assembly is distinct from that previously noted for the transthyretin protein family. However, structural comparisons and bacterial two-hybrid data suggest that the SmLip tetramer is not relevant to its role as a core component of the type VI secretion system, but rather reflects a propensity for SmLip to participate in protein-protein interactions. A relatively low level of sequence conservation amongst Lip homologues is noted and is restricted to parts of the structure that might be involved in interactions with physiological partners.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee DD1 5EH, Scotland.