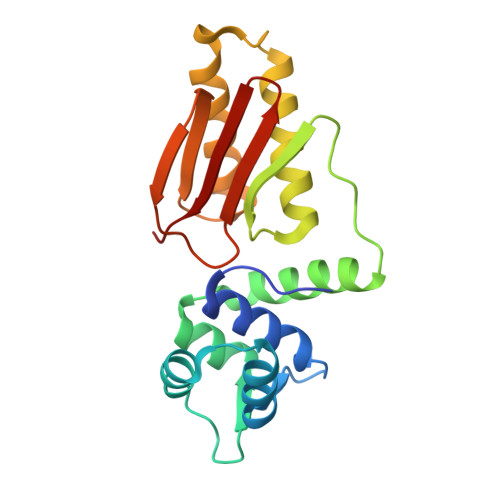
Structural Insights and Calcium-Switching Mechanism of Fasciola hepatica Calcium-Binding Protein FhCaBP4.
Shin, B., Park, S., Park, I., Shin, H., Bang, K., Kim, S., Hwang, K.Y.(2025) Int J Mol Sci 26
- PubMed: 40806711
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157584
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9VOA - PubMed Abstract:
Fasciola hepatica remains a global health and economic concern, and treatment still relies heavily on triclabendazole. At the parasite-host interface, F. hepatica calcium-binding proteins (FhCaBPs) have a unique EF-hand/DLC-like domain fusion found only in trematodes. This makes it a parasite-specific target for small compounds and vaccinations. To enable novel therapeutic strategies, we report the first elevated-resolution structure of a full-length FhCaBP4. The apo structure was determined at 1.93 Å resolution, revealing a homodimer architecture that integrates an N-terminal, calmodulin-like, EF-hand pair with a C-terminal dynein light chain (DLC)-like domain. Structure-guided in silico mutagenesis identified a flexible, 16-residue β4-β5 loop (LTGSYWMKFSHEPFMS) with an FSHEPF core that demonstrates greater energetic variability than its FhCaBP2 counterpart, likely explaining the distinct ligand-binding profiles of these paralogs. Molecular dynamics simulations and AlphaFold3 modeling suggest that EF-hand 2 acts as the primary calcium-binding site, with calcium coordination inducing partial rigidification and modest expansion of the protein structure. Microscale thermophoresis confirmed calcium as the major ligand, while calmodulin antagonists bound with lower affinity and praziquantel demonstrated no interaction. Thermal shift assays revealed calcium-dependent stabilization and a merger of biphasic unfolding transitions. These results suggest that FhCaBP4 functions as a calcium-responsive signaling hub, with an allosterically coupled EF-hand-DLC interface that could serve as a structurally tractable platform for drug targeting in trematodes.
- Department of Biotechnology, College of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul 02841, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: