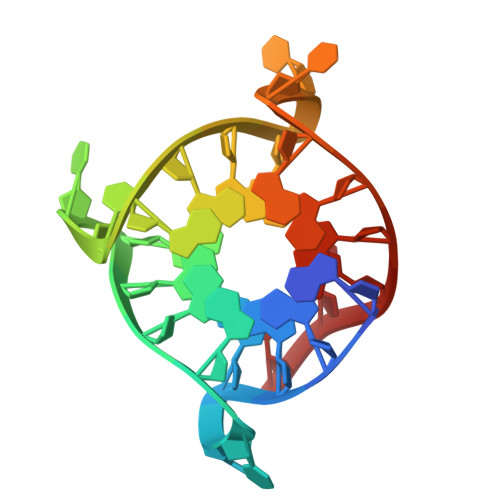
Crystal structures of distinct parallel and antiparallel DNA G-quadruplexes reveal structural polymorphism in C9orf72 G4C2 repeats.
Geng, Y., Liu, C., Miao, H., Suen, M.C., Xie, Y., Zhang, B., Han, W., Wu, C., Ren, H., Chen, X., Tai, H.C., Wang, Z., Zhu, G., Cai, Q.(2025) Nucleic Acids Res 53
- PubMed: 40930530
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf879
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9UK6, 9UK8 - PubMed Abstract:
The abnormal expansion of GGGGCC (G4C2) repeats in the noncoding region of the C9orf72 gene is a major genetic cause of two devastating neurodegenerative disorders, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). These G4C2 repeats are known to form G-quadruplex (G4) structures, which are hypothesized to contribute to disease pathogenesis. Here, we demonstrated that four DNA G4C2 repeats can fold into two structurally distinct G4 conformations: a parallel and an antiparallel topology. The high-resolution crystal structure of the parallel G4 reveals an eight-layered dimeric assembly, formed by two identical monomeric units. Each unit contains four stacked G-tetrads connected by three propeller CC loops and is stabilized through 5'-to-5' π-π interactions and coordination with a central K+ ion. Notably, the 3'-ending cytosines form a C·C+·C·C+ quadruple base pair stacking onto the adjacent G-tetrad layer. In contrast, the antiparallel G4 adopts a four-layered monomeric structure with three edgewise loops, where the C6 and C18 bases engage in stacking interaction with neighboring G-tetrad via a K+ ion. These structurally distinct G-quadruplexes provide mechanistic insights into C9orf72-associated neurodegeneration and offer potential targets for the development of structure-based therapeutic strategies for ALS and FTD.
- Clinical Research Institute of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Fujian Key Laboratory of Brain Tumors Diagnosis and Precision Treatment, Xiamen Key Laboratory of Brain Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, School of Public Health, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361003, Fujian, China.
Organizational Affiliation: