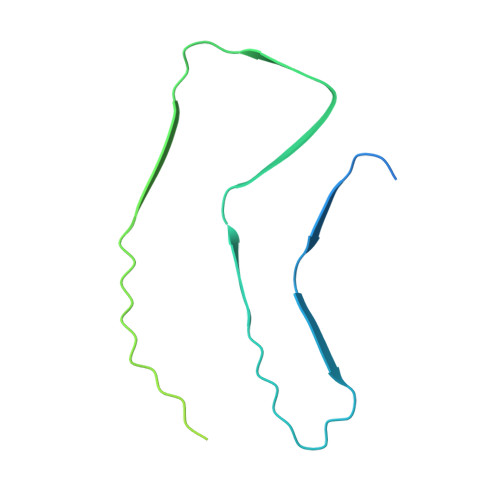
Cryo-EM structure of amyloid fibrils formed by full-length human alpha A-crystallin with pathogenic mutation R116C.
Song, M., Han, J., Cao, Q.(2025) Commun Chem 8: 233-233
- PubMed: 40770067
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-025-01637-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9U4L - PubMed Abstract:
The aggregation of crystallin proteins in human lens is the primary cause of cataracts, a disease that leads to blindness of tens of millions of people worldwide. Understanding the molecular architectures of these aggregated crystallin proteins can facilitate the development of therapeutic drugs to treat cataract without surgery. In this study, we prepared two types of crystallin fibrils, thick and thin, using recombinant human αA-crystallin harboring the disease-associated R116C mutation under neutral and acidic conditions, respectively. The structure of the thin fibrils was determined via cryo-EM at a resolution of 3.7 Å, whereas the thick fibrils appeared unsuitable for cryo-EM structure determination. Structure analysis suggests that the thin fibrils adopt a three-layered structure stabilized by extensive steric zipper interactions. The observation of aspartate and glutamate ladders stacking along the fibril axis is consistent with the preference for an acidic environment of the thin fibrils. Disease mutations on Arg49 and Arg54 appear to facilitate the fibril structure, suggesting the potential disease relevance of these fibrils. Taken together, our study provides the first near-atomic resolution structure of aggregated crystallin and may facilitate the future studies on the mechanism and therapeutic of cataracts.
- Bio-X Institutes, Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Ministry of Education, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: