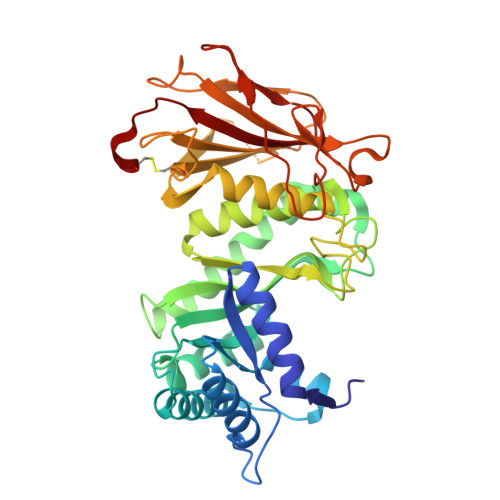
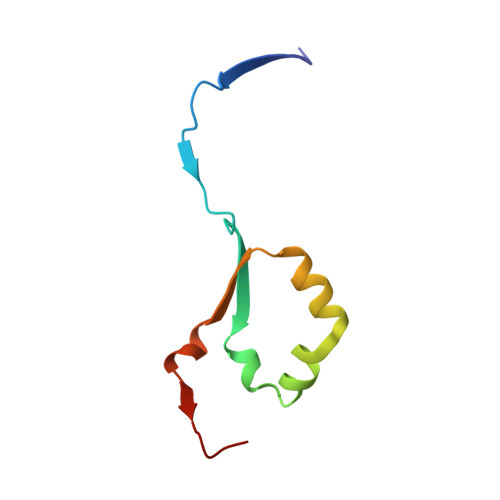
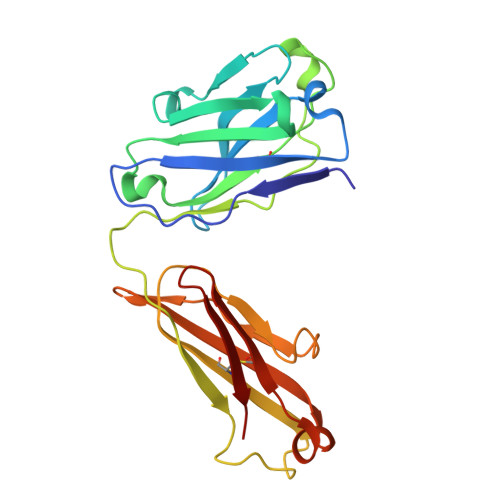
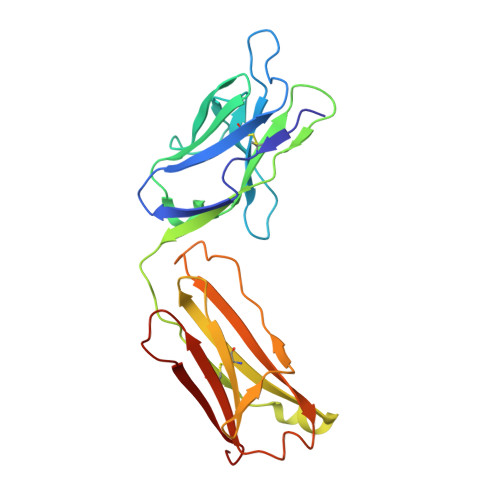
Heparanase-Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody (mAb A54) Attenuates Tumor Growth and Metastasis.
Barash, U., Farhoud, M., Odeh, M., Huberman, E., Wu, L., Vlodavsky, I.(2025) Cells 14
- PubMed: 40940793
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171379
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9S8W - PubMed Abstract:
Heparanase is the only human enzyme responsible for heparan sulfate (HS) breakdown, an activity that remodels the extracellular matrix (ECM) and strongly drives cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Compelling evidence implies that heparanase promotes essentially all aspects of the tumorigenic process, namely, tumor initiation, vascularization, growth, metastasis, and chemoresistance. A key mechanism by which heparanase accelerates cancer progression is by enabling the release and bioavailability of HS-bound growth factors, chemokines, and cytokines, residing in the tumor microenvironment and supporting tumor growth and metastasis. The currently available heparanase inhibitors are mostly HS/heparin-like compounds that lack specificity and exert multiple off-target side effects. To date, only four such compounds have progressed to clinical trials, and none have been approved for clinical use. We have generated and characterized an anti-heparanase monoclonal antibody (A54 mAb) that specifically inhibits heparanase enzymatic activity (ECM degradation assay) and cellular uptake. Importantly, A54 mAb attenuates xenograft tumor growth and metastasis (myeloma, glioma, pancreatic, and breast carcinomas) primarily when administered (syngeneic or immunocompromised mice) in combination with conventional anti-cancer drugs. Co-crystallization of the A54 Fab fragment and the heparanase enzyme revealed that the interaction between the two proteins takes place adjacent to the enzyme HS/heparin binding domain II (HBDII; Pro271-Ala276), likely hindering heparanase from interacting with HS substrates via steric occlusion of the active site cleft. Collectively, we have generated and characterized a novel mAb that specifically neutralizes heparanase enzymatic activity and attenuates its pro-tumorigenic effects in preclinical models, paving the way for its clinical examination against cancer, inflammation, and other diseases.
- Technion Integrated Cancer Center (TICC), Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Haifa 31096, Israel.
Organizational Affiliation: