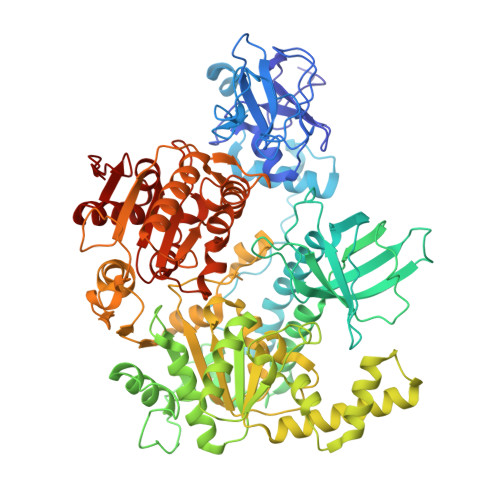
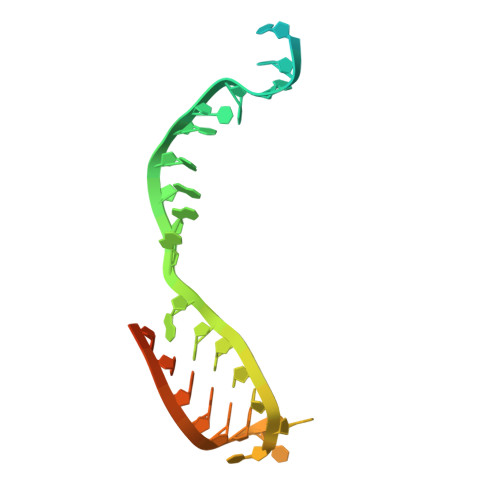
Mechanistic insights into recruitment and regulation of the RNA helicase UPF1 in replication-dependent histone mRNA decay.
Machado de Amorim, A., Xue, G., He, W., Dittmers, T., Lewandowski, S., Perez-Borrajero, C., Bethmann, J., Mateva, N., Krage, C., Nandana, V., Loll, B., Hilal, T., Hennig, J., Urlaub, H., Marzluff, W.F., Chakrabarti, S.(2026) Nat Commun 17: 155-155
- PubMed: 41484129
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67991-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9QWN - PubMed Abstract:
Metazoan histone mRNAs are a unique class of mRNAs that lack the poly(A) tail present in all other eukaryotic transcripts. Instead, they end in a conserved stem-loop (SL) structure, necessitating a decay mechanism that is distinct from deadenylation-initiated degradation. Here, combining structural and functional approaches, we elucidate molecular mechanisms of initiation of histone mRNA decay. At the end of S-phase, the RNA helicase UPF1, the exoribonuclease 3'hExo and stem-loop binding protein SLBP all contribute to histone mRNA degradation, although how they are mechanistically coupled remained unknown. The cryoEM structure of an UPF1:SL RNA complex, presented here, shows that binding of UPF1 partially melts the RNA stem in the absence of ATP, harnessing the free energy derived from RNA-binding to unwind RNA. This melting event primes the SL-RNA for decay by 3'hExo. Using biochemical and cellular analyses, we demonstrate that SLBP directly engages the UPF1 helicase core to attenuate its unwinding activity and prevent premature degradation. Activation of UPF1 at a later stage promotes SL-RNA decay. We provide direct evidence that UPF1, SLBP and 3'hExo form a degradosome-like assembly that functionally couples SL unwinding and degradation, highlighting a dynamic and intricate network of UPF1-centric interactions that orchestrates timely histone mRNA decay.
- Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Department of Biology, Chemistry and Pharmacy, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: