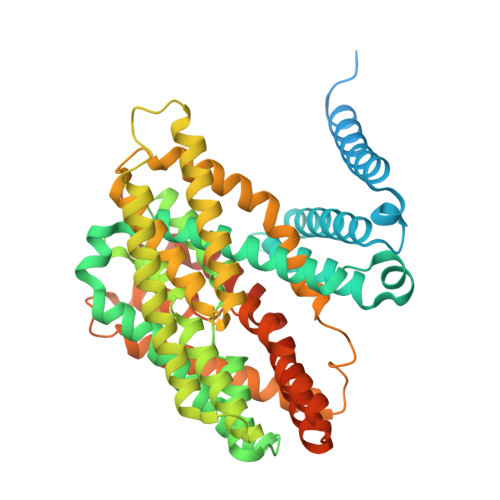
Structure and Inhibition of the Human Na + /H + Exchanger SLC9B2.
Jung, S., Kokane, S., Li, H., Iwata, S., Nomura, N., Drew, D.(2025) Int J Mol Sci 26
- PubMed: 40362458
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094221
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9QUB, 9QUW - PubMed Abstract:
The sodium/proton exchanger NHA2, also known as SLC9B2, is important for insulin secretion, renal blood pressure regulation, and electrolyte retention. Recent structures of bison NHA2 has revealed its unique 14-transmembrane helix architecture, which is different from SLC9A/NHE members made up from 13-TM helices. Sodium/proton exchangers are functional homodimers, and the additional N-terminal helix in NHA2 was found to alter homodimer assembly. Here, we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of apo human NHA2 in complex with a Fab fragment and also with the inhibitor phloretin bound at 2.8 and 2.9 Å resolution, respectively. We show how phosphatidic acid (PA) lipids bind to the homodimer interface of NHA2 on the extracellular side, which we propose has a regulatory role linked to cell volume regulation. The ion binding site of human NHA2 has a salt bridge interaction between the ion binding aspartate D278 and R432, an interaction previously broken in the bison NHA2 structure, and these differences suggest a possible ion coupling mechanism. Lastly, the human NHA2 structure in complex with phloretin offers a template for structure-guided drug design, potentially leading to the development of more selective and potent NHA2 inhibitors.
- Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Science for Life Laboratory, Stockholm University, 171-65 Stockholm, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: