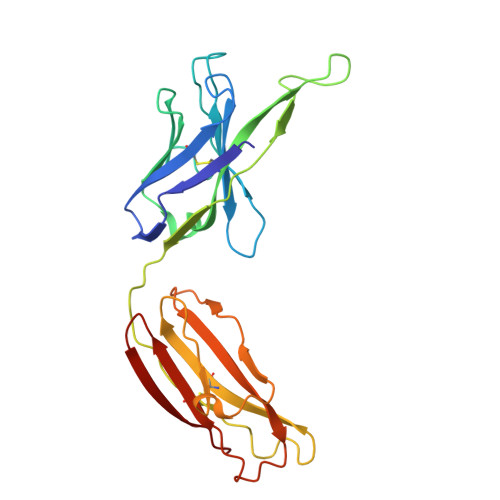
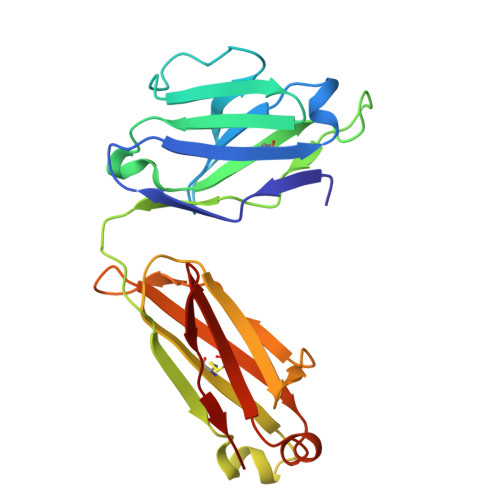
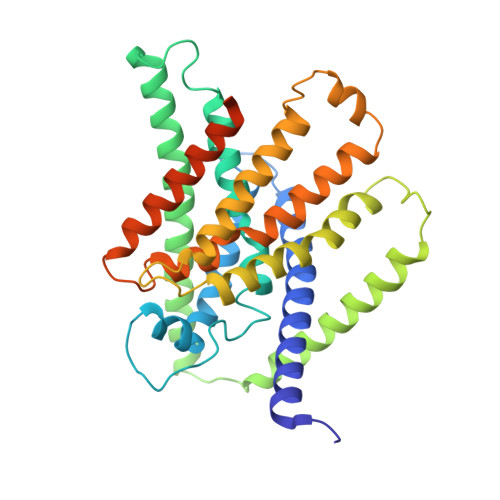
The molecular mechanism of fluoride export by the eukaryotic fluoride channel FEX.
Kang, C.Y., An, M., Heidari, S., Torabifard, H., Ohi, M.D., Stockbridge, R.B.(2025) Nat Commun
- PubMed: 41381451
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67289-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9OP1 - PubMed Abstract:
Much of life on Earth, including plants, fungi, and bacteria, evolved to resist toxic environmental fluoride. In eukaryotes, the major resistance mechanism is fluoride export by membrane proteins known as FEX. Using electrophysiology and transport assays, we establish that FEX from plants and yeasts are highly selective fluoride channels. Fluoride transport activity depends on reversible sodium ion binding, but sodium itself is not transported. We determine a structure of a FEX protein, from pathogenic yeast Candida albicans, using cryo-EM. Bolstered by mutagenesis studies, this structure reveals a fluoride permeation route through a single phenylalanine-lined pore. Molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate that a cation binding motif adjacent to the pore provides a stable sodium binding site that is accessible from the external aqueous solution. Comparison to the structurally related bacterial fluoride channels, Flucs, provides a glimpse of the evolution of structural and mechanistic complexity in a membrane protein family with inverted repeat architecture.
- Program in Biophysics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: