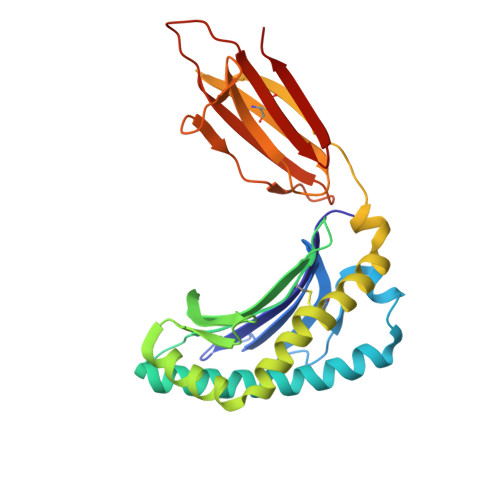
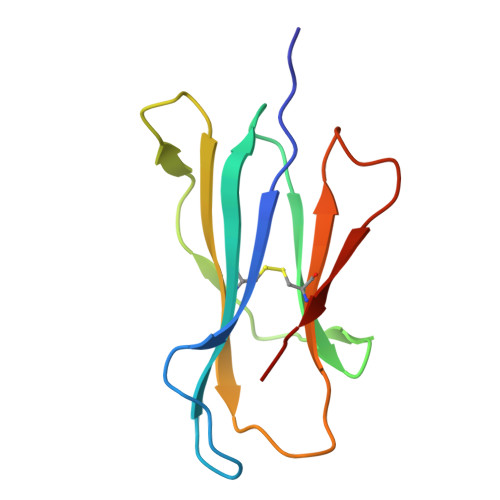
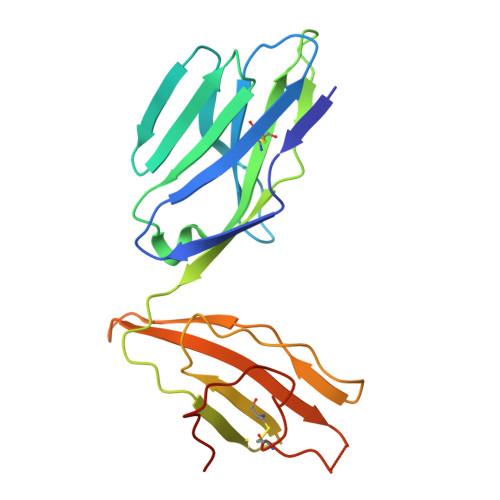
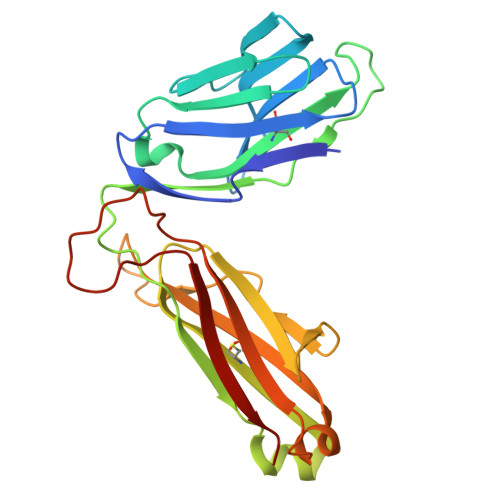
The antigen-presenting molecule MR1 binds host-generated riboflavin catabolites.
Abdelaal, M.R., Deng, J., McInerney, M.P., Ito, E., Purcell, A.W., Yamasaki, S., Villadangos, J.A., McWilliam, H.E.G., Gherardin, N.A., Rossjohn, J., Awad, W.(2026) J Exp Medicine 223
- PubMed: 41295949
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20250711
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9O05, 9O06, 9O07, 9O08 - PubMed Abstract:
MHC class I-related protein (MR1) presents vitamin B-based antigens (Ags) to mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells. While microbial riboflavin (RF) precursors are well-documented MR1 ligands, it is unclear whether host-generated RF catabolites influence MR1 immunity. Here, we report that RF catabolites, including 10-formylmethylflavin (FMF), lumichrome, lumiflavin, and alloxazine, bind to MR1 with moderate affinity, while RF itself binds weakly. In contrast to the MR1-upregulating microbial RF precursors, RF catabolites reduced the surface level of MR1 by inducing its retention in the endoplasmic reticulum and inhibiting exit. These RF catabolites weakly competed with vitamin B-based Ags for MR1 binding, thereby selectively inhibiting MAIT activation. The crystal structures of MR1 with RF, FMF, lumiflavin, and lumichrome show binding in the A'-pocket of MR1. Here, lumichrome formed a "flavin bond" covalent interaction with MR1-Lys43 differing from the typical Schiff base. Collectively, we identified three-ringed isoalloxazines that bind MR1 and reduce surface levels, suggesting a potential role in dampening MAIT cell immunity.
- Infection and Immunity Program and Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Monash University, Clayton, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: