Mycobacterium tuberculosis CrgA Forms a Dimeric Structure with Its Transmembrane Domain Sandwiched between Cytoplasmic and Periplasmic beta-Sheets, Enabling Multiple Interactions with Other Divisome Proteins.
Shin, Y., Prasad, R., Das, N., Taylor, J.A., Qin, H., Hu, W., Hu, Y.Y., Fu, R., Zhang, R., Zhou, H.X., Cross, T.A.(2025) J Am Chem Soc 147: 11117-11131
- PubMed: 40106808
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c17168
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9NM2 - PubMed Abstract:
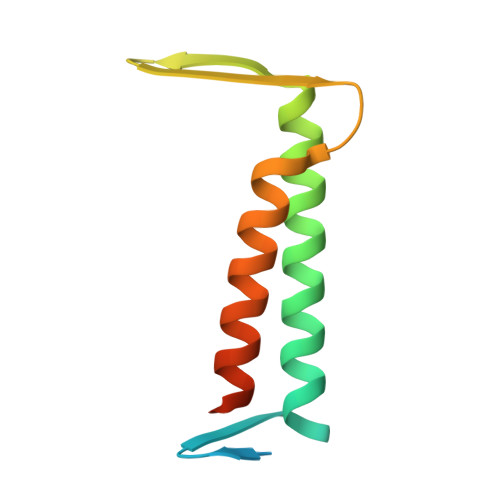
CrgA is a key transmembrane (TM) protein in the cell division process of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ( Mtb ), the pathogen responsible for tuberculosis. While many of the Mtb divisome proteins have been identified, their structures and interactions remain largely unknown. Previous studies of CrgA using oriented-sample solid-state NMR have defined the tilt and rotation of the TM helices, but the cytoplasmic and periplasmic domains and even the oligomeric state were uncharacterized. Here, by combining oriented-sample and magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR spectra, we solved the full-length structure of CrgA. The structure features a dimer with a TM domain sandwiched between a cytoplasmic β-sheet and a periplasmic β-sheet. The β-sheets stabilize dimerization, which in turn increases CrgA's ability to participate in multiple protein interactions. Within the membrane, CrgA binds FtsQ, CwsA, PbpA, FtsI, and MmPL3 via its TM helices; in the cytoplasm, Lys23 and Lys25 project outward from the β-sheet to interact with acidic residues of FtsQ and FtsZ. The structural determination of CrgA thus provides significant insights into its roles in recruiting other divisome proteins and stabilizing their complexes for Mtb cell wall synthesis and polar growth.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida 32306, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: