Anti-M1R/B6R antibody characterization and bispecific design for enhanced orthopoxvirus protection.
Zhao, R., Wu, L., Zhang, Y., Ma, J., Liu, D., Zheng, Y., Kong, T., Ma, R., Gao, Z., Chai, Y., Liu, Y., Tian, Y., Xia, Y., Hou, Y., Lu, J., Cong, Z., Huang, B., Tan, W., Xue, J., Gao, G.F., Wang, Q.(2025) EMBO Mol Med 17: 2713-2734
- PubMed: 40921877
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44321-025-00299-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
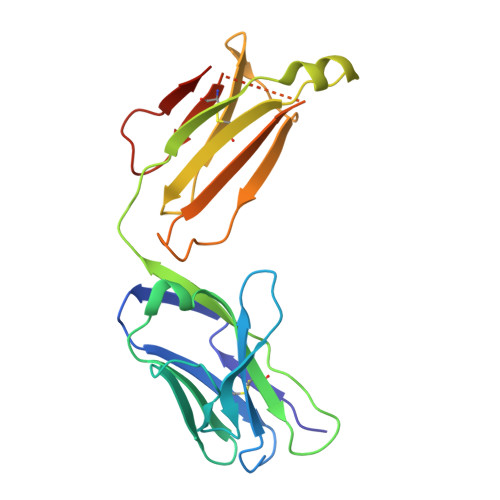
9LF8, 9VHZ - PubMed Abstract:
The global outbreak of the mpox in humans, caused by the mpox virus (MPXV), underscores the urgent need for safe and effective therapeutics. In this study, we characterized the dominant MPXV immunogens, M1R and B6R, by sequencing monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) from the immunized mice and analyzing their epitopes and functions through in vitro and in vivo assessments of binding and antiviral activities. Several broadly effective anti-M1R and anti-B6R neutralizing MAbs were identified and they exhibited enhanced antiviral effects against MPXV or vaccinia virus (VACV) when used in antibody cocktail and bispecific antibody designs. Notably, the VH-CH1 switch region-inserting format of bispecific antibodies exhibited robust protective efficacy against VACV in a mouse model. Collectively, our study characterized the epitope and functional maps of anti-M1R and anti-B6R MAbs and developed promising broad-spectrum antibody candidates for the treatment of MPXV and other orthopoxvirus infections.
- Institute of Physical Science and Information, Anhui University, 230039, Hefei, Anhui, China.
Organizational Affiliation: