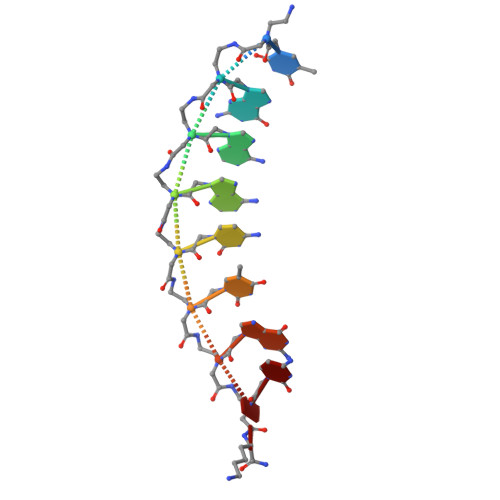
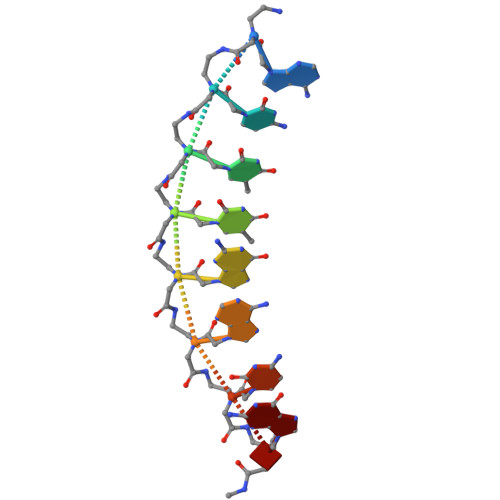
Peptide nucleic acids in parallel orientation form invasion complexes with double-stranded DNA.
Shibata, M., Sugimoto, H., Hibino, M., Shoji, O., Aiba, Y.(2025) RSC Chem Biol 6: 1566-1575
- PubMed: 40901609
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5cb00172b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9L5Z - PubMed Abstract:
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is a unique class of synthetic nucleic acids with a pseudo-peptide backbone, known for its high nucleic acid recognition capability and its ability to directly recognize double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) via the formation of a unique invasion complex. While most natural and artificial nucleic acids form duplexes in an antiparallel configuration due to the general instability of parallel configurations, PNA distinctively forms both antiparallel and parallel duplexes. In this study, we focused on this previously underexplored property of PNA to adopt a parallel duplex configuration and developed a novel double-duplex invasion strategy by leveraging the differences in thermal stability between the antiparallel and parallel orientations of PNA duplexes. Furthermore, we report the first crystal structure of a parallel PNA duplex, which was found to exhibit different structural features compared to the previously characterized antiparallel PNA duplex. This study highlights the potential of artificial nucleic acids in dsDNA recognition and demonstrates that the parallel architecture may serve as a conceptual foundation for advancing broader methodological innovations in nucleic acid research.
- Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, Furo-cho Chikusa-ku Nagoya 464-8602 Japan aiba.yuichiro.f4@f.mail.nagoya-u.ac.jp +81-52-789-3557 +81-52-789-2953.
Organizational Affiliation: