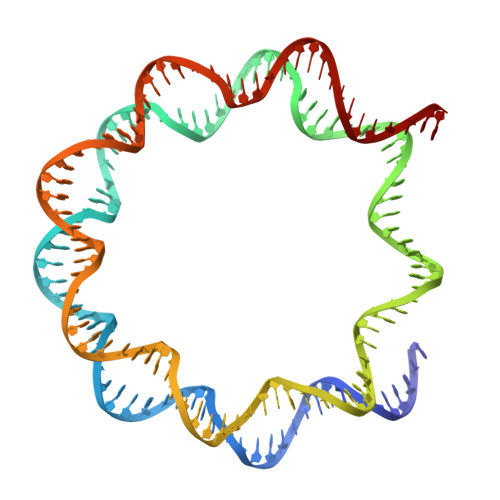
Allosteric activation of RNF20/RNF40-RAD6A-mediated H2BK120 monoubiquitylation by H2BS112 GlcNAcylation.
Deng, Z., Tao, S., Du, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, L., Shi, Q., Du, X., Sun, M., Tong, Z., Pan, M., Liu, L., Ai, H.(2026) Nat Chem Biol
- PubMed: 41495224
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-025-02109-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9KQO - PubMed Abstract:
The activation of H2B K120 monoubiquitylation (H2BK120ub) by H2B S112 GlcNAcylation (H2BS112GlcNAc) has an important role in regulating transcriptional activation, yet its mechanism remains unclear. Here we chemically synthesized H2BS112GlcNAc-modified nucleosomes and quantitatively evaluated how H2BS112GlcNAc stimulates ubiquitylation by RNF20/RNF40-RAD6A E3-E2 enzymes. Cryo-electron microscopy determination of a chemically trapped RNF20/RNF40-RAD6A-Ub-H2BS112GlcNAc nucleosome complex revealed that the H2BS112GlcNAc moiety interacts with the E2 enzyme RAD6A but not the E3 ligase RNF20/RNF40. Mutagenesis and kinetics analyses demonstrated that H2BS112GlcNAc allosterically stimulates ubiquitin transfer from the RAD6A~Ub thioester to H2B K120 by enhancing the nucleophilicity of H2B K120. Structure‒activity relationship analysis further identified the essential roles of the C2 N-acetyl group and the β-configuration of C1 on the H2BS112GlcNAc moiety. These findings provide the structural evidence of histone posttranslational modification crosstalk involving O-GlcNAcylation and reveal how O-GlcNAcylation can allosterically stimulate enzyme activity through substrate modification.
- School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Institute of Translational Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Antibody-Drug Conjugates with Innovative Target, Shanghai Frontiers Science Center of Drug Target Identification and Delivery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: