Generation of shark single-domain antibodies as an aid for Cryo-EM structure determination of membrane proteins: Use hyaluronan synthase as an example.
Deng, P., Zhang, X., Wen, J., Xu, M., Li, P., Wang, H., Bi, Y.(2025) J Struct Biol X 11: 100126-100126
- PubMed: 40475323
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjsbx.2025.100126
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9KQC - PubMed Abstract:
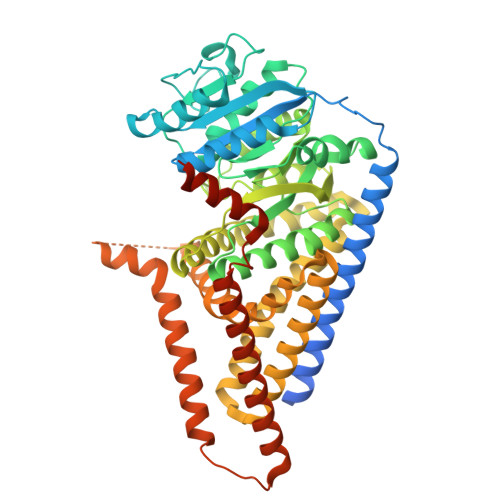
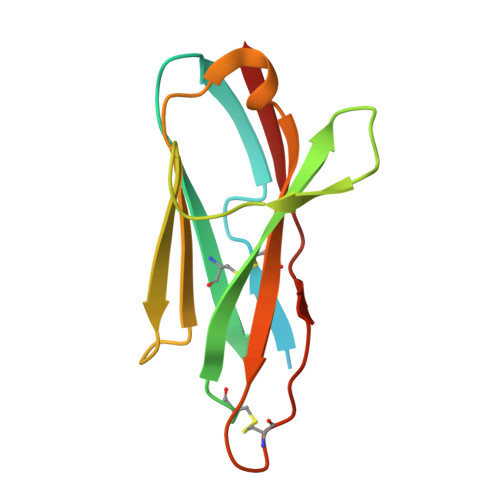
In cartilaginous fish, the immunoglobulin new antigen receptor (IgNAR) is naturally devoid of light chains. The variable regions of IgNAR (VNARs) are solely responsible for antigen recognition, similar to VHHs (variable domain of the heavy chain of heavy-chain antibodies) in camelids. Although VNARs have attracted growing interest, generating VNARs against membrane proteins remains challenging. Furthermore, the structure of a VNAR in complex with a membrane protein has not yet been reported. This study features a membrane protein, Chlorella virus hyaluronan synthase (CvHAS), and provides a comprehensive methodological approach to generate its specific shark VNARs, addressing several major concerns and important optimizations. We showed that shark physiological urea pressure was tolerable for CvHAS, and indirect immobilization was strongly preferred over passive adsorption for membrane proteins. Together with optimizations to improve mononuclear cell (MC) viability and VNAR expression efficiency, we successfully generated S2F6, a CvHAS-specific VNAR with nM-level high affinity. The structure of the CvHAS-S2F6 complex was then determined by cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM), reporting the first membrane protein and VNAR complex structure. It shows that S2F6 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of CvHAS, with a different epitope than the reported CvHAS-specific VHHs. This study provides valuable insights into developing VNARs for membrane proteins and their applications in structural biology.
- CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, PR China.
Organizational Affiliation: