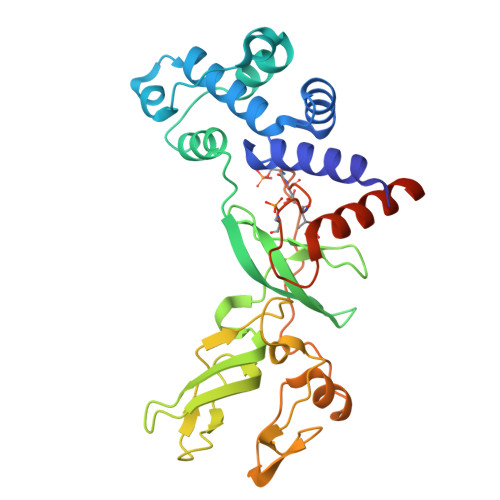
Phosphorylation of shiftless is important for inhibiting the programmed -1 ribosomal frameshift.
Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Chong, H., Hou, P., Hao, W., Li, M., Liu, Z., Jia, W., Qin, B., He, Y., Cui, S.(2025) Sci Adv 11: eadw7471-eadw7471
- PubMed: 41417896
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adw7471
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9KBO - PubMed Abstract:
Shiftless (SFL) is a broad-spectrum inhibitor of programmed -1 ribosomal frameshift (-1 PRF) and exhibits various antiviral activities. Here, we characterized human SFL structurally and biochemically. The 2.0-angstrom resolution crystal structure of SFL reveals a boat-like module comprising an N-terminal helical bundle and three zinc fingers at the C terminus. A hyperphosphorylation loop (HPL) buried between the helical bundle and the zinc finger 1 harbors four phosphorylated residues (p-S249, p-T250 p-T253, and p-S256), which are important to protein folding. SFL forms monomers in solution and binds the HIV-1 -1 PRF sequence with nanomolar affinity ( K D = 5.7 nanomolar). Disruption of HPL phosphorylation decreased the RNA binding affinity and undermined the SFL-mediated -1 PRF inhibition of various viruses. Proximity-dependent biotinylation identified three cellular Ser/Thr kinases-EEF2K, NEK9, and PBK-that phosphorylate SFL in cells. These findings shed light on the mechanisms underlying -1 PRF regulation by SFL and provide insights into the role of SFL in virus inhibition.
- NHC Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens, National Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China.
Organizational Affiliation: