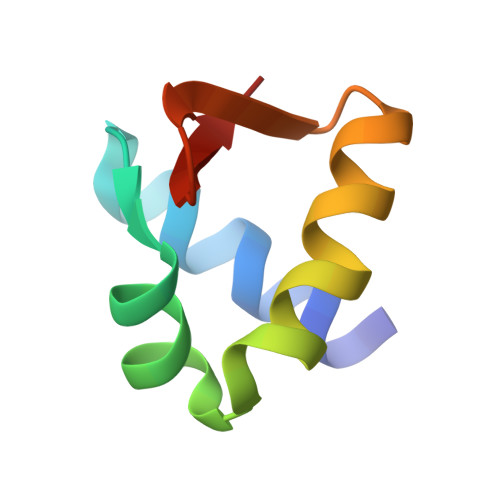
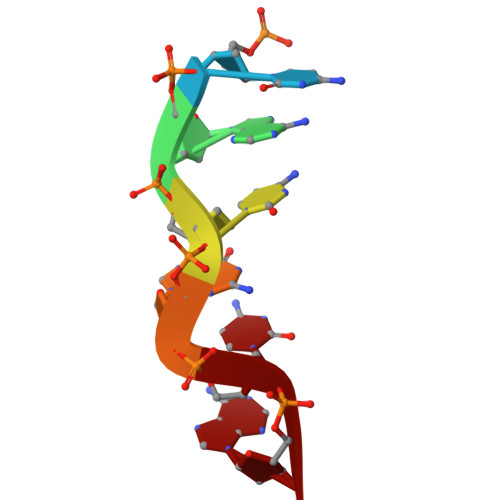
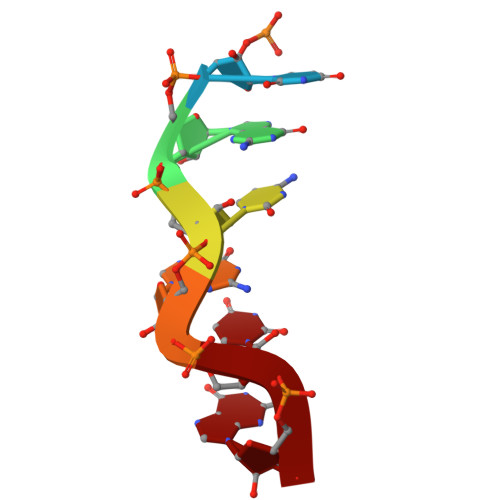
ZBP1 senses spliceosome stress through Z-RNA:DNA hybrid recognition.
He, J., Zhu, Y., Tian, Z., Liu, M., Gao, A., Fu, W., Lu, F., Sun, Y., Guo, Y., Pan, R., Ji, Y., Chen, J., Lu, H., Lin, J., Liang, X., Kim, C., Zhou, C., Jiao, H.(2025) Mol Cell 85: 1790-1805.e7
- PubMed: 40267921
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2025.04.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9J89, 9J8G - PubMed Abstract:
Z-DNA-binding protein 1 (ZBP1; also known as DAI or DLM-1) regulates cell death and inflammation by sensing left-handed double-helical nucleic acids, including Z-RNA and Z-DNA. However, the physiological conditions that generate Z-form nucleic acids (Z-NAs) and activate ZBP1-dependent signaling pathways remain largely elusive. In this study, we developed a probe, Zα-mFc, that specifically detected both Z-DNA and Z-RNA. Utilizing this probe, we discovered that inhibiting spliceosome causes nuclear accumulation of Z-RNA:DNA hybrids, which are sensed by ZBP1 via its Zα domains, triggering apoptosis and necroptosis in mammalian cells. Furthermore, we solved crystal structures of the human or mouse Zα1 domain complexed with a 6-bp RNA:DNA hybrid, revealing that the RNA:DNA hybrid adopts a left-handed conformation. Our findings demonstrate that the spliceosome acts as a checkpoint preventing accumulation of Z-RNA:DNA hybrids, which potentially function as endogenous ligands activating ZBP1-dependent cell death pathways.
- Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Molecular Cancer Biology, Life Sciences Institute, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China; Department of Neonatal Surgery, Children's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou 310052, China.
Organizational Affiliation: