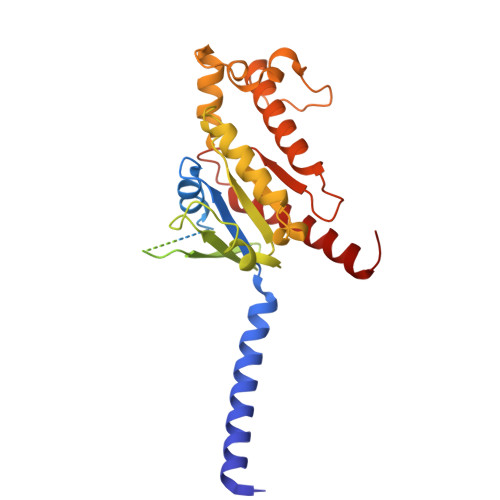
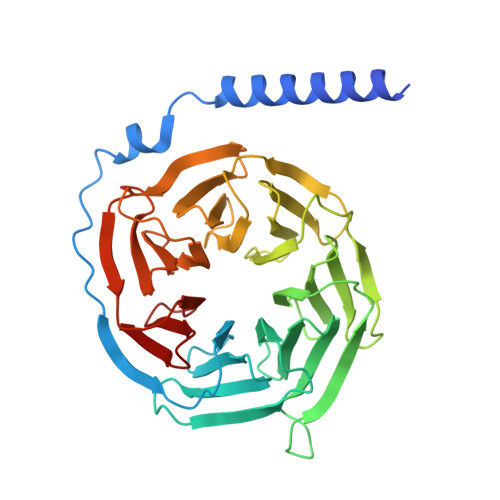
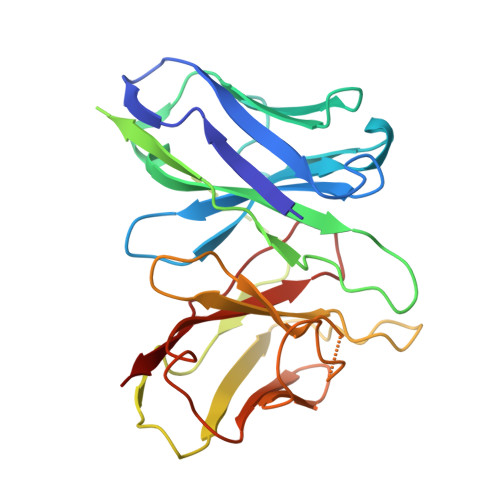
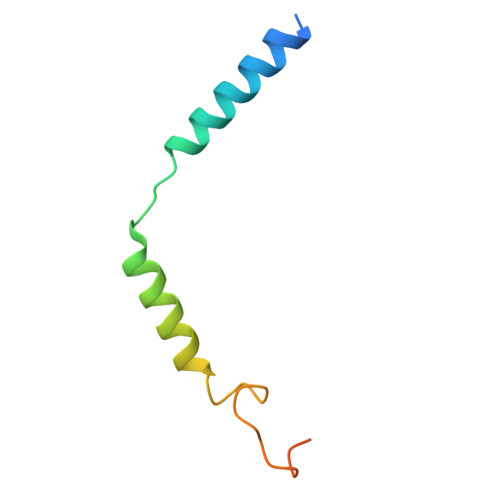
Structural basis of the cysteinyl leukotriene receptor type 2 activation by LTD4.
Jiang, M., Xu, Y., Luan, X., Wu, K., Li, Z., Xu, H.E., Zhang, S., Jiang, Y., Yin, W.(2025) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 122: e2417148122-e2417148122
- PubMed: 40193607
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2417148122
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9IXX - PubMed Abstract:
The G protein-coupled cysteinyl leukotriene receptor CysLT2R plays intricate roles in the physiology and pathogenesis of inflammation-related processes. It has garnered increasing attention as a potential therapeutic target for atopic asthma, brain injury, central nervous system disorders, and various types of cancer. In this study, we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the cysteinyl leukotriene D4 (LTD4)-bound human CysLT2R in complex with a Gα q protein, adopting an active conformation at a resolution of 3.15 Å. The structure elucidates a spacious polar pocket designed to accommodate the two branched negative ends of LTD4 and reveals a lateral ligand access route into the orthosteric pocket located on transmembrane domain helix (TM) 4 and 5. Furthermore, our findings highlight the crucial role of transmembrane domain helix 3 in sensing agonist moieties, representing the pivotal mechanism of receptor activation for both CysLT1R and CysLT2R. Collectively, the insights derived from our structural investigation establish a foundation for comprehending CysLT2R activation by its endogenous ligand LTD4, offering a rational basis for the design of drugs targeting CysLT2R.
- Lingang Laboratory, Shanghai 200031, China.
Organizational Affiliation: