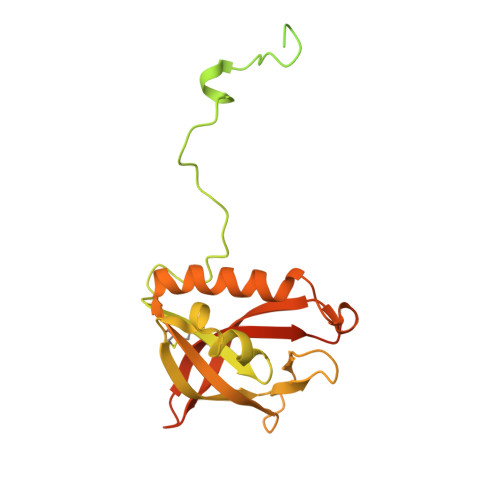
The Paulinella chromatophore transit peptide part2 adopts a structural fold similar to the gamma-glutamyl-cyclotransferase fold.
Klimenko, V., Reiners, J., Applegate, V., Reimann, K., Popowicz, G., Hoeppner, A., Papadopoulos, A., Smits, S.H.J., Nowack, E.C.M.(2025) Plant Physiol 199
- PubMed: 41071934
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiaf504
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9I08, 9I09 - PubMed Abstract:
The chromatophores of the cercozoan amoeba Paulinella are photosynthetic organelles that evolved from a cyanobacterial endosymbiont. Many nucleus-encoded chromatophore-targeted proteins carry unusual N-terminal targeting signals termed crTPs, which are bipartite. crTPpart1 likely mediates trafficking through the secretory pathway and is cleaved off during import, but crTPpart2 remains attached to its cargo protein and its function is unknown. To unravel the functional role of crTPpart2, here we elucidated the structures of crTPpart2 from two different chromatophore-targeted proteins by X-ray crystallography at ∼2.3 Å resolution. Interestingly, the crTPpart2 of both proteins adopts a structural fold. Both structures share a conserved structured core and a flexible N-terminal arm. The structured core resembles proteins of the γ-glutamyl cyclotransferase superfamily within which crTPpart2 structures form a protein (sub)-family. The proposed catalytic center typical for proteins with cyclotransferase activity is not conserved in crTPpart2. A Cys pair that is conserved in crTPpart2 of many chromatophore-targeted proteins has been captured as a disulfide bridge. Together, our data suggest that chromatophore-targeted proteins are imported in their folded state and that the fold adopted by crTPpart2 plays a functional role during import. The characterization of its structure and flexibility provides important steps toward elucidating this protein translocation mechanism.
- Institute of Microbial Cell Biology, Department of Biology, Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, 40225 Düsseldorf, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: