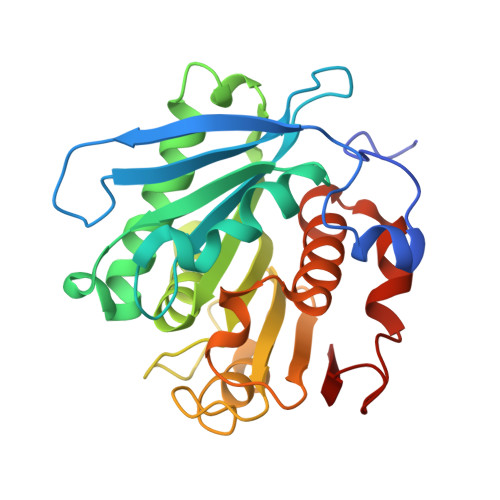
Functional and Structural Characterization of PETase SM14 from Marine-Sponge Streptomyces sp. Active on Polyethylene Terephthalate.
Carletti, A., Bhattacharya, S., Pedroni, S., Berto, M., Bonettini, R., Castagna, R., Parisini, E., Di Rocco, G.(2025) ACS Sustain Chem Eng 13: 7460-7468
- PubMed: 40443410
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5c00737
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9HYD - PubMed Abstract:
The recent discovery of the PETase enzyme family offers a sustainable solution for depolymerizing poly-(ethylene terephthalate) (PET), one of the most widespread plastic compounds, under mild conditions. This enables the environmentally beneficial conversion of plastic waste into value-added products. Among this enzyme family, PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis has been the most extensively studied. Although other similar enzymes have been discovered, our knowledge about the catalytic and structural properties of this class remains limited. In this study, a PETase-like enzyme (PETase SM14) from Streptomyces sp. SM14 was heterologously produced in Escherichia coli, and its activity was tested on post-consumer plastic substrates using high-performance liquid chromatography for product quantification as well as scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy for substrate surface imaging evaluation. PETase SM14 exhibited high salt tolerance (1.5 M), good heat resistance (Tm 56.26 °C), and optimal activity at pH 9.0, highlighting its potential for PET waste bioremediation. Furthermore, its X-ray crystal structure was solved at 1.43 Å resolution, revealing conserved features of the PETase family with potential relevance for future engineering applications.
- Department of Life Sciences, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Via Campi 103, 41125 Modena, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: