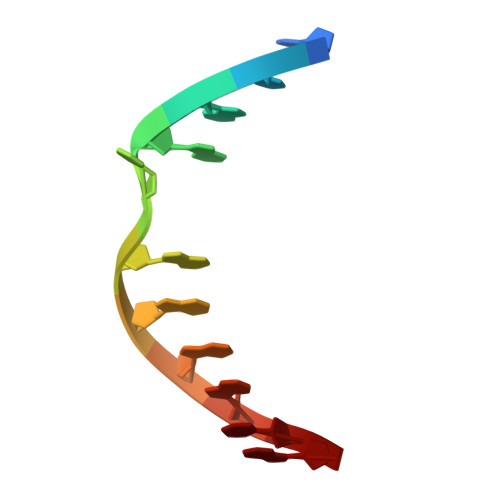
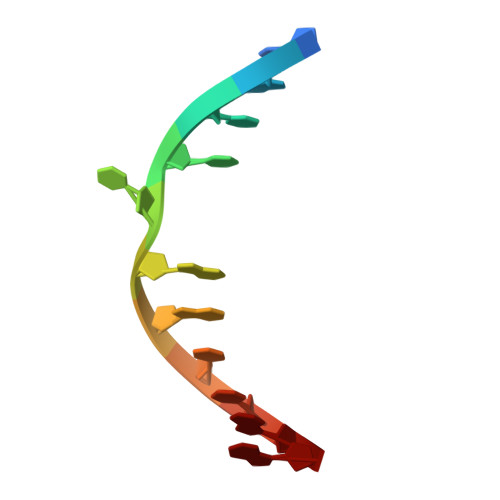
NMR-Based Rational Drug Design of G:G Mismatch DNA Binding Ligand Trapping Transient Complex via Disruption of a Key Allosteric Interaction.
Sakurabayashi, S., Furuita, K., Yamada, T., Sugiura, N., Nomura, M., Nakane, T., Kawamoto, A., Kurisu, G., Miyanoiri, Y., Fujiwara, T., Nakatani, K., Kojima, C.(2025) J Am Chem Soc 147: 14254-14269
- PubMed: 40245052
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c17538
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ZD2, 8ZD7, 8ZD8 - PubMed Abstract:
Small molecules that bind to mismatched DNA have been applied in various fields, including nanotechnology, bioimaging, and therapeutics. However, the intrinsic dynamic nature of mismatched DNA complicates the prediction of structural changes upon ligand binding, hindering rational ligand design. In this study, NMR was used for structure-based drug design, with a focus on the G:G mismatch binder ND and the structural dynamics of the DNA- ND complex. Through comprehensive NMR analysis with isotope labeling, two complex structures, the transient and stable complexes, were successfully determined. The nucleobase flip-outs and the distortion of the phosphate backbone of the complex structures were characterized by residual dipolar coupling (RDC) and 31 P NMR, respectively. The RDC-refined stable complex structure suggested that the ligand linker-nucleobase interaction allosterically regulates a structural transition. This interaction was experimentally validated by 1 H- 15 N HSQC spectra using a 15 N-labeled ligand. Disruption of this key allosteric interaction facilitated the design of a new ligand, sND , that traps the transient complex structure. In conclusion, comprehensive NMR analysis using a weak binder aids in designing nucleic acid-binding ligands based on transient complex structures.
- Department of Regulatory Bioorganic Chemistry, The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research (SANKEN), Osaka University, 8-1 Mihogaoka, Osaka, Ibaraki 567-0047, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: