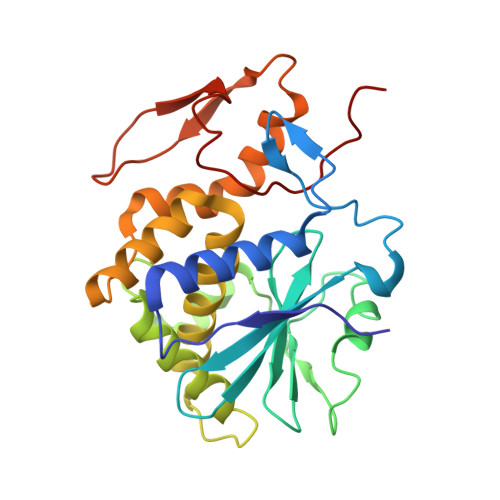
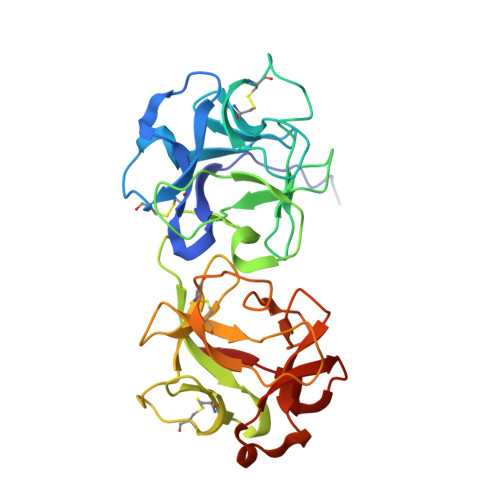
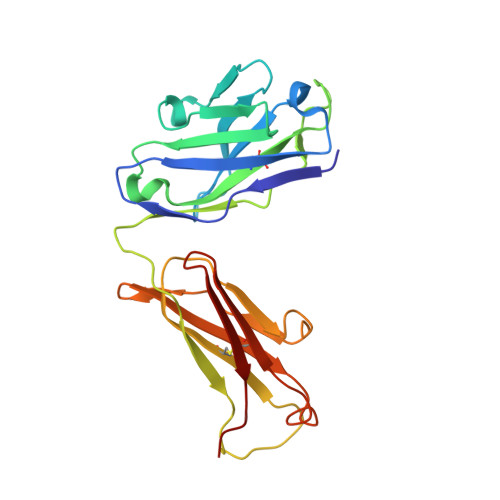
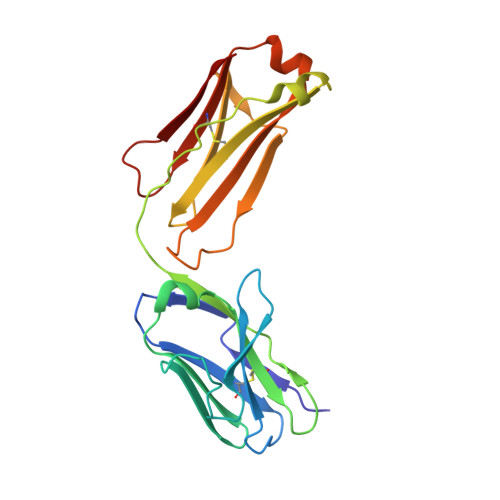
Structural Basis of Antibody-Mediated Inhibition of Ricin Toxin Attachment to Host Cells.
Vance, D.J., Rudolph, M.J., Davis, S.A., Mantis, N.J.(2023) Biochemistry 62: 3181-3187
- PubMed: 37903428
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00480
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TFH, 8TFL - PubMed Abstract:
Monoclonal antibodies, JB4 and SylH3, neutralize ricin toxin (RT) by inhibiting the galactose-specific lectin activity of the B subunit of the toxin (RTB), which is required for cell attachment and entry. It is not immediately apparent how the antibodies accomplish this feat, considering that RTB consists of two globular domains (D1, D2) each divided into three homologous subdomains (α, β, γ) with the two functional galactosyl-specific carbohydrate recognition domains (CRDs) situated on opposite poles (subdomains 1α and 2γ). Here, we report the X-ray crystal structures of JB4 and SylH3 Fab fragments bound to RTB in the context of RT. The structures revealed that neither Fab obstructed nor induced detectable conformational alterations in subdomains 1α or 2γ. Rather, JB4 and SylH3 Fabs recognize nearly identical epitopes within an ancillary carbohydrate recognition pocket located in subdomain 1β. Despite limited amino acid sequence similarity between SylH3 and JB4 Fabs, each paratope inserts a Phe side chain from the heavy (H) chain complementarity determining region (CDR3) into the 1β CRD pocket, resulting in local aromatic stacking interactions that potentially mimic a ligand interaction. Reconciling the fact that stoichiometric amounts of SylH3 and JB4 are sufficient to disarm RTB's lectin activity without evidence of allostery, we propose that subdomain 1β functions as a "coreceptor" required to stabilize glycan interactions principally mediated by subdomains 1α and 2γ. Further investigation into subdomain 1β will yield fundamental insights into the large family of R-type lectins and open novel avenues for countermeasures aimed at preventing toxin uptake into vulnerable tissues and cells.
- Division of Infectious Diseases, Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health, Albany, New York 12208, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: