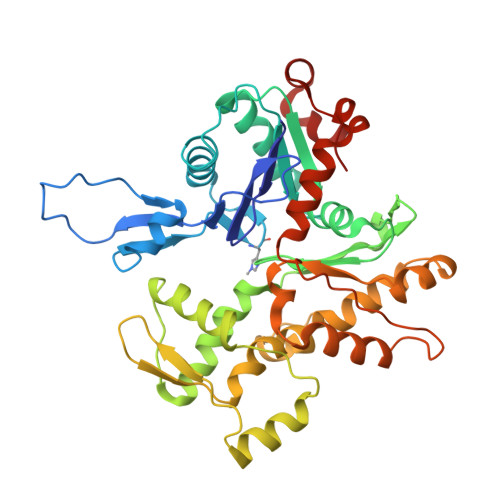
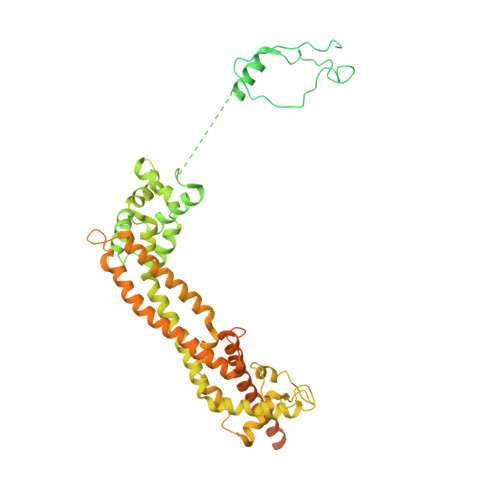
Molecular mechanism of actin filament elongation by formins.
Oosterheert, W., Boiero Sanders, M., Funk, J., Prumbaum, D., Raunser, S., Bieling, P.(2024) Science 384: eadn9560-eadn9560
- PubMed: 38603491
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adn9560
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8RTT, 8RTY, 8RU0, 8RU2, 8RV2 - PubMed Abstract:
Formins control the assembly of actin filaments (F-actin) that drive cell morphogenesis and motility in eukaryotes. However, their molecular interaction with F-actin and their mechanism of action remain unclear. In this work, we present high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of F-actin barbed ends bound by three distinct formins, revealing a common asymmetric formin conformation imposed by the filament. Formation of new intersubunit contacts during actin polymerization sterically displaces formin and triggers its translocation. This "undock-and-lock" mechanism explains how actin-filament growth is coordinated with formin movement. Filament elongation speeds are controlled by the positioning and stability of actin-formin interfaces, which distinguish fast and slow formins. Furthermore, we provide a structure of the actin-formin-profilin ring complex, which resolves how profilin is rapidly released from the barbed end during filament elongation.
- Department of Structural Biochemistry, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology, 44227 Dortmund, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: