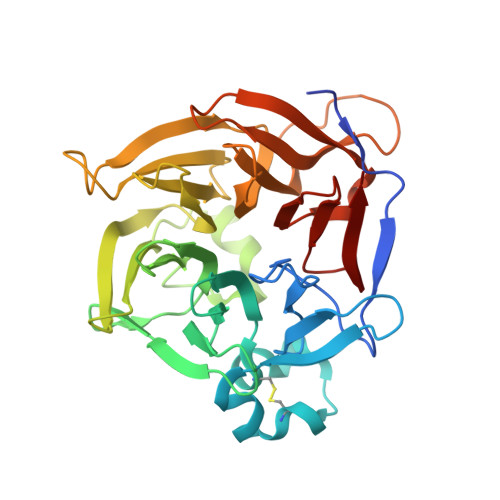
THOUSAND-GRAIN WEIGHT 6, which is an IAA-glucose hydrolase, preferentially recognizes the structure of the indole ring.
Akabane, T., Suzuki, N., Ikeda, K., Yonezawa, T., Nagatoishi, S., Matsumura, H., Yoshizawa, T., Tsuchiya, W., Kamino, S., Tsumoto, K., Ishimaru, K., Katoh, E., Hirotsu, N.(2024) Sci Rep 14: 6778-6778
- PubMed: 38514802
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-57506-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8KG3 - PubMed Abstract:
An indole-3-acetic acid (IAA)-glucose hydrolase, THOUSAND-GRAIN WEIGHT 6 (TGW6), negatively regulates the grain weight in rice. TGW6 has been used as a target for breeding increased rice yield. Moreover, the activity of TGW6 has been thought to involve auxin homeostasis, yet the details of this putative TGW6 activity remain unclear. Here, we show the three-dimensional structure and substrate preference of TGW6 using X-ray crystallography, thermal shift assays and fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance ( 19 F NMR). The crystal structure of TGW6 was determined at 2.6 Å resolution and exhibited a six-bladed β-propeller structure. Thermal shift assays revealed that TGW6 preferably interacted with indole compounds among the tested substrates, enzyme products and their analogs. Further analysis using 19 F NMR with 1,134 fluorinated fragments emphasized the importance of indole fragments in recognition by TGW6. Finally, docking simulation analyses of the substrate and related fragments in the presence of TGW6 supported the interaction specificity for indole compounds. Herein, we describe the structure and substrate preference of TGW6 for interacting with indole fragments during substrate recognition. Uncovering the molecular details of TGW6 activity will stimulate the use of this enzyme for increasing crop yields and contributes to functional studies of IAA glycoconjugate hydrolases in auxin homeostasis.
- Graduate School of Life Sciences, Toyo University, 1-1-1 Izumino, Itakura, Oura, Gunma, 374-0193, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: