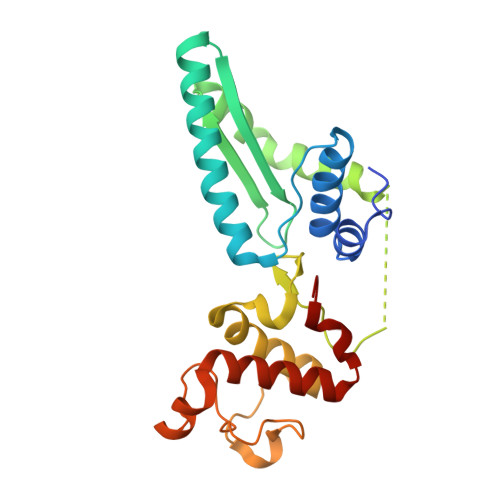
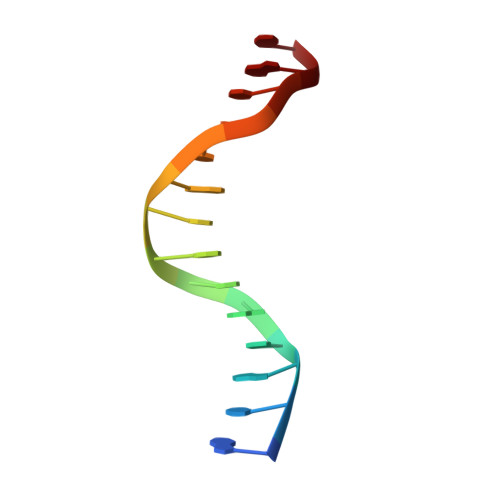
Molecular mechanism of specific DNA sequence recognition by NRF1.
Liu, K., Li, W., Xiao, Y., Lei, M., Zhang, M., Min, J.(2024) Nucleic Acids Res 52: 953-966
- PubMed: 38055835
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad1162
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8K3D, 8K4L - PubMed Abstract:
Nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) regulates the expression of genes that are vital for mitochondrial biogenesis, respiration, and various other cellular processes. While NRF1 has been reported to bind specifically to GC-rich promoters as a homodimer, the precise molecular mechanism governing its recognition of target gene promoters has remained elusive. To unravel the recognition mechanism, we have determined the crystal structure of the NRF1 homodimer bound to an ATGCGCATGCGCAT dsDNA. In this complex, NRF1 utilizes a flexible linker to connect its dimerization domain (DD) and DNA binding domain (DBD). This configuration allows one NRF1 monomer to adopt a U-turn conformation, facilitating the homodimer to specifically bind to the two TGCGC motifs in the GCGCATGCGC consensus sequence from opposite directions. Strikingly, while the NRF1 DBD alone could also bind to the half-site (TGCGC) DNA of the consensus sequence, the cooperativity between DD and DBD is essential for the binding of the intact GCGCATGCGC sequence and the transcriptional activity of NRF1. Taken together, our results elucidate the molecular mechanism by which NRF1 recognizes specific DNA sequences in the promoters to regulate gene expression.
- Hubei Key Laboratory of Genetic Regulation and Integrative Biology, School of Life Sciences, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, PR China.
Organizational Affiliation: