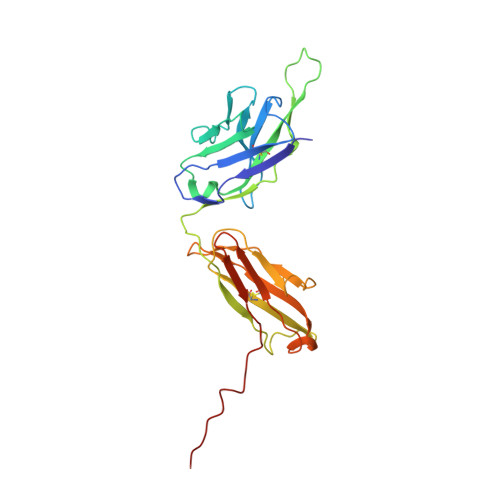
A potent Henipavirus cross-neutralizing antibody reveals a dynamic fusion-triggering pattern of the G-tetramer.
Fan, P., Sun, M., Zhang, X., Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Yao, Y., Li, M., Fang, T., Sun, B., Chen, Z., Chi, X., Chen, L., Peng, C., Chen, Z., Zhang, G., Ren, Y., Liu, Z., Li, Y., Li, J., Li, E., Guan, W., Li, S., Gong, R., Zhang, K., Yu, C., Chiu, S.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 4330-4330
- PubMed: 38773072
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48601-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8K0C, 8K0D, 8XC4 - PubMed Abstract:
The Hendra and Nipah viruses (HNVs) are highly pathogenic pathogens without approved interventions for human use. In addition, the interaction pattern between the attachment (G) and fusion (F) glycoproteins required for virus entry remains unclear. Here, we isolate a panel of Macaca-derived G-specific antibodies that cross-neutralize HNVs via multiple mechanisms. The most potent antibody, 1E5, confers adequate protection against the Nipah virus challenge in female hamsters. Crystallography demonstrates that 1E5 has a highly similar binding pattern to the receptor. In cryo-electron microscopy studies, the tendency of 1E5 to bind to the upper or lower heads results in two distinct quaternary structures of G. Furthermore, we identify the extended outer loop β1S2-β1S3 of G and two pockets on the apical region of fusion (F) glycoprotein as the essential sites for G-F interactions. This work highlights promising drug candidates against HNVs and contributes deeper insights into the viruses.
- Laboratory of Advanced Biotechnology, Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing, China. fanpengfei93@163.com.
Organizational Affiliation: