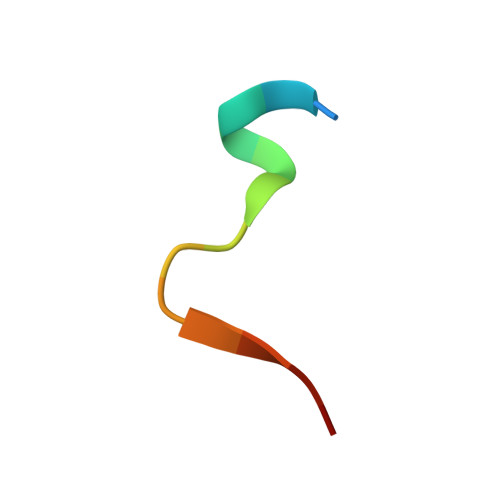
Complementary hydrophobic interaction of the redox enzyme maturation protein NarJ with the signal peptide of the respiratory nitrate reductase NarG.
Song, W.S., Kim, J.H., Namgung, B., Cho, H.Y., Shin, H., Oh, H.B., Ha, N.C., Yoon, S.I.(2024) Int J Biol Macromol 262: 129620-129620
- PubMed: 38262549
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129620
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JZC, 8JZD - PubMed Abstract:
In bacteria, NarJ plays an essential role as a redox enzyme maturation protein in the assembly of the nitrate reductase NarGHI by interacting with the N-terminal signal peptide of NarG to facilitate cofactor incorporation into NarG. The purpose of our research was to elucidate the exact mechanism of NarG signal peptide recognition by NarJ. We determined the structures of NarJ alone and in complex with the signal peptide of NarG via X-ray crystallography and verified the NarJ-NarG interaction through mutational, binding, and molecular dynamics simulation studies. NarJ adopts a curved α-helix bundle structure with a U-shaped hydrophobic groove on its concave side. This groove accommodates the signal peptide of NarG via a dual binding mode in which the left and right parts of the NarJ groove each interact with two consecutive hydrophobic residues from the N- and C-terminal regions of the NarG signal peptide, respectively, through shape and chemical complementarity. This binding is accompanied by unwinding of the helical structure of the NarG signal peptide and by stabilization of the NarG-binding loop of NarJ. We conclude that NarJ recognizes the NarG signal peptide through a complementary hydrophobic interaction mechanism that mediates a structural rearrangement.
- Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: