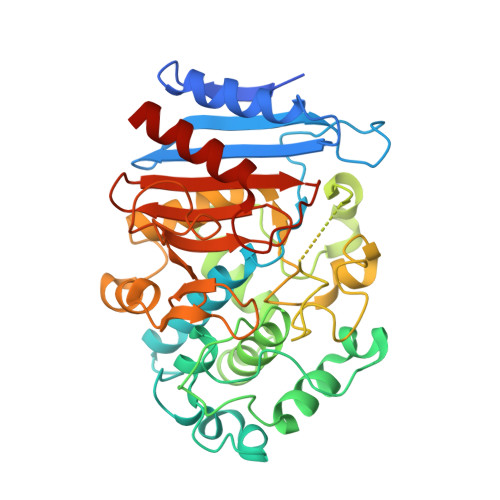
Crystal Structure of EstZF172 Catalyzing Stereoselectively ( R )‐CNDE in Pregabalin Biosynthesis.
Liang, Z., Ma, X., Sun, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, G., Chi, C.(2025) ACS Omega 10: 21693-21700
- PubMed: 40488026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.5c01054
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8J5V - PubMed Abstract:
Pregabalin has garnered extensive clinical application for the management of neuropathic pain and epilepsy owing to its high efficacy and broad drug concentration range. EstZF172 is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of pregabalin, capable of stereoselectively catalyzing the production of ( R )-CCMA from the key intermediate rac -CNDE. The novel crystal structure of EstZF172 indicates that it contains a highly conserved Ser-Lys-Tyr catalytic triad and belongs to the family VIII 2 carboxylesterases. Molecular docking demonstrates that the steric hindrance presented by residues I159 and F239 plays a crucial role in influencing the binding affinity of the chiral substrate ( R )-CNDE for the catalytic site. The study provides a structural basis and reference for the stereoselective catalysis of EstZF172 and engineering modification of the key enzyme in the synthesis of pregabalin.
- Department of Bioengineering and Biotechnology, Huaqiao University, Jimei Ave. 668, Xiamen 361021, China.
Organizational Affiliation: