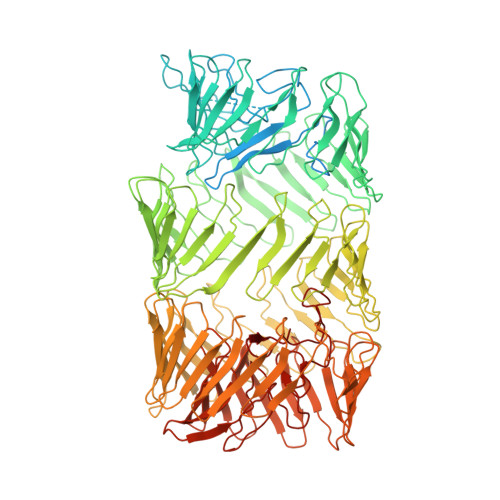
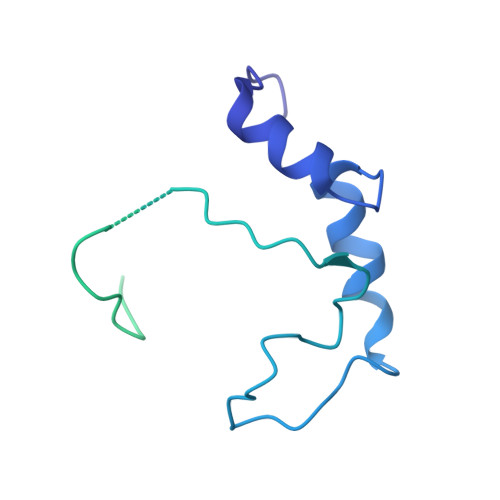
Vibrio parahaemolyticus prey targeting requires autoproteolysis-triggered dimerization of the type VI secretion system effector RhsP.
Tang, L., Dong, S., Rasheed, N., Wu, H.W., Zhou, N., Li, H., Wang, M., Zheng, J., He, J., Chao, W.C.H.(2022) Cell Rep 41: 111732-111732
- PubMed: 36476863
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111732
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8H8A, 8H8B, 8H8C - PubMed Abstract:
The rearrangement hotspot (Rhs) repeat is an ancient giant protein fold found in all domains of life. Rhs proteins are polymorphic toxins that could either be deployed as an ABC complex or via a type VI secretion system (T6SS) in interbacterial competitions. To explore the mechanism of T6SS-delivered Rhs toxins, we used the gastroenteritis-associated Vibrio parahaemolyticus as a model organism and identified an Rhs toxin-immunity pair, RhsP-RhsP I . Our data show that RhsP-dependent prey targeting by V. parahaemolyticus requires T6SS2. RhsP can bind to VgrG2 independently without a chaperone and spontaneously self-cleaves into three fragments. The toxic C-terminal fragment (RhsP C ) can bind to VgrG2 via a VgrG2-interacting region (VIR). Our electron microscopy (EM) analysis reveals that the VIR is encapsulated inside the Rhs β barrel structure and that autoproteolysis triggers a dramatic conformational change of the VIR. This alternative VIR conformation promotes RhsP dimerization, which significantly contributes to T6SS2-mediated prey targeting by V. parahaemolyticus.
- Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Macau SAR, China; Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Infectious Diseases and Molecular Immunopathology, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China.
Organizational Affiliation: