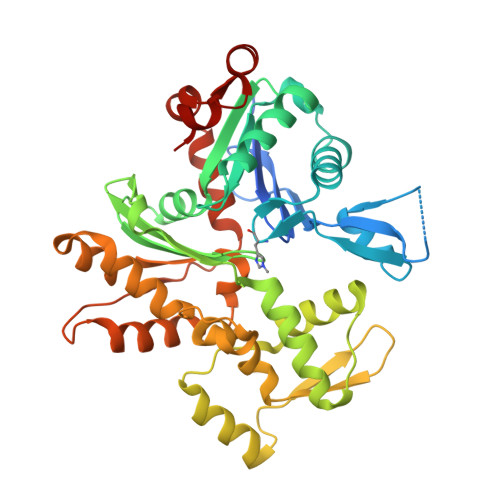
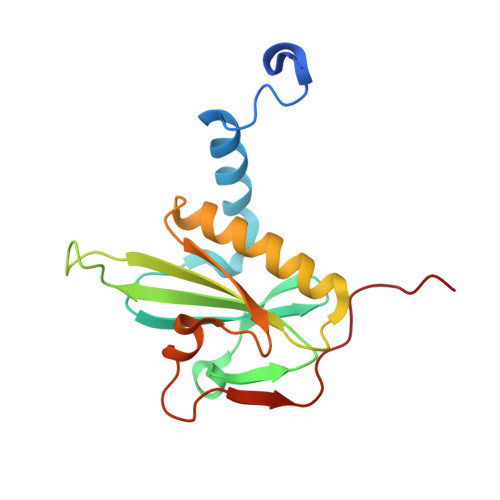
Mutagenic analysis of actin reveals the mechanism of His161 flipping that triggers ATP hydrolysis.
Iwasa, M., Takeda, S., Narita, A., Maeda, Y., Oda, T.(2023) Front Cell Dev Biol 11: 1105460-1105460
- PubMed: 37009486
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2023.1105460
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GSU, 8GSW, 8GT1, 8GT2, 8GT3, 8GT4, 8GT5 - PubMed Abstract:
The dynamic assembly of actin is controlled by the hydrolysis of ATP, bound to the center of the molecule. Upon polymerization, actin undergoes a conformational change from the monomeric G-form to the fibrous F-form, which is associated with the flipping of the side chain of His161 toward ATP. His161 flipping from the gauche-minus to gauche-plus conformation leads to a rearrangement of the active site water molecules, including ATP attacking water (W1), into an orientation capable of hydrolysis. We previously showed that by using a human cardiac muscle α-actin expression system, mutations in the Pro-rich loop residues (A108G and P109A) and in a residue that was hydrogen-bonded to W1 (Q137A) affect the rate of polymerization and ATP hydrolysis. Here, we report the crystal structures of the three mutant actins bound to AMPPNP or ADP-P i determined at a resolution of 1.35-1.55 Å, which are stabilized in the F-form conformation with the aid of the fragmin F1 domain. In A108G, His161 remained non-flipped despite the global actin conformation adopting the F-form, demonstrating that the side chain of His161 is flipped to avoid a steric clash with the methyl group of A108. Because of the non-flipped His161, W1 was located away from ATP, similar to G-actin, which was accompanied by incomplete hydrolysis. In P109A, the absence of the bulky proline ring allowed His161 to be positioned near the Pro-rich loop, with a minor influence on ATPase activity. In Q137A, two water molecules replaced the side-chain oxygen and nitrogen of Gln137 almost exactly at their positions; consequently, the active site structure, including the W1 position, is essentially conserved. This seemingly contradictory observation to the reported low ATPase activity of the Q137A filament could be attributed to a high fluctuation of the active site water. Together, our results suggest that the elaborate structural design of the active site residues ensures the precise control of the ATPase activity of actin.
- Graduate School of Informatics, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: