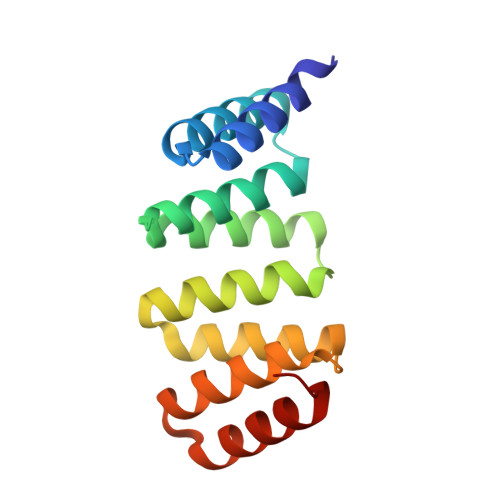
Fast and versatile sequence-independent protein docking for nanomaterials design using RPXDock.
Sheffler, W., Yang, E.C., Dowling, Q., Hsia, Y., Fries, C.N., Stanislaw, J., Langowski, M.D., Brandys, M., Li, Z., Skotheim, R., Borst, A.J., Khmelinskaia, A., King, N.P., Baker, D.(2023) PLoS Comput Biol 19: e1010680-e1010680
- PubMed: 37216343
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010680
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FWD - PubMed Abstract:
Computationally designed multi-subunit assemblies have shown considerable promise for a variety of applications, including a new generation of potent vaccines. One of the major routes to such materials is rigid body sequence-independent docking of cyclic oligomers into architectures with point group or lattice symmetries. Current methods for docking and designing such assemblies are tailored to specific classes of symmetry and are difficult to modify for novel applications. Here we describe RPXDock, a fast, flexible, and modular software package for sequence-independent rigid-body protein docking across a wide range of symmetric architectures that is easily customizable for further development. RPXDock uses an efficient hierarchical search and a residue-pair transform (RPX) scoring method to rapidly search through multidimensional docking space. We describe the structure of the software, provide practical guidelines for its use, and describe the available functionalities including a variety of score functions and filtering tools that can be used to guide and refine docking results towards desired configurations.
- Institute for Protein Design, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: