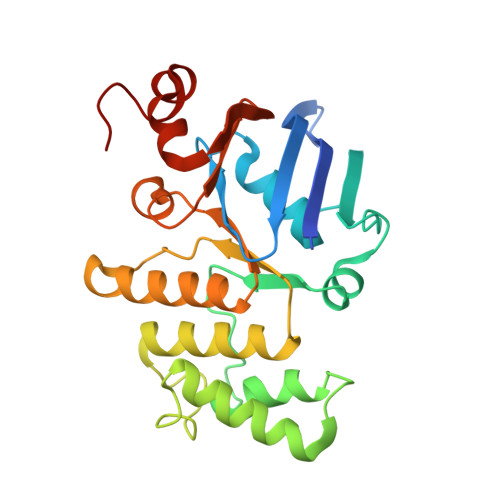
A new antibiotic traps lipopolysaccharide in its intermembrane transporter.
Pahil, K.S., Gilman, M.S.A., Baidin, V., Clairfeuille, T., Mattei, P., Bieniossek, C., Dey, F., Muri, D., Baettig, R., Lobritz, M., Bradley, K., Kruse, A.C., Kahne, D.(2024) Nature 625: 572-577
- PubMed: 38172635
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06799-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FRL, 8FRM, 8FRN, 8FRO, 8FRP, 8UFG, 8UFH - PubMed Abstract:
Gram-negative bacteria are extraordinarily difficult to kill because their cytoplasmic membrane is surrounded by an outer membrane that blocks the entry of most antibiotics. The impenetrable nature of the outer membrane is due to the presence of a large, amphipathic glycolipid called lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in its outer leaflet 1 . Assembly of the outer membrane requires transport of LPS across a protein bridge that spans from the cytoplasmic membrane to the cell surface. Maintaining outer membrane integrity is essential for bacterial cell viability, and its disruption can increase susceptibility to other antibiotics 2-6 . Thus, inhibitors of the seven lipopolysaccharide transport (Lpt) proteins that form this transenvelope transporter have long been sought. A new class of antibiotics that targets the LPS transport machine in Acinetobacter was recently identified. Here, using structural, biochemical and genetic approaches, we show that these antibiotics trap a substrate-bound conformation of the LPS transporter that stalls this machine. The inhibitors accomplish this by recognizing a composite binding site made up of both the Lpt transporter and its LPS substrate. Collectively, our findings identify an unusual mechanism of lipid transport inhibition, reveal a druggable conformation of the Lpt transporter and provide the foundation for extending this class of antibiotics to other Gram-negative pathogens.
- Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: