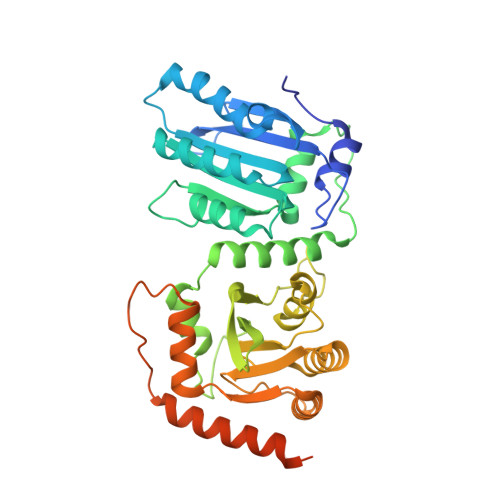
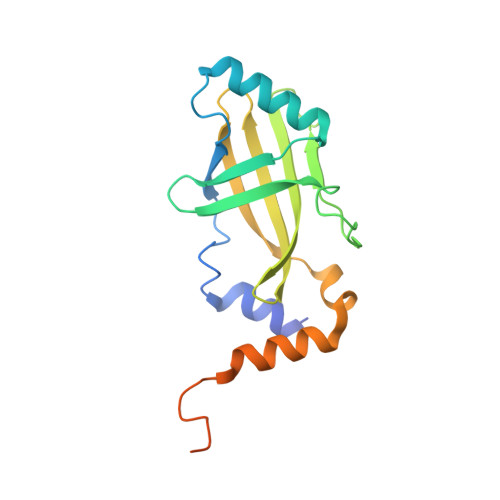
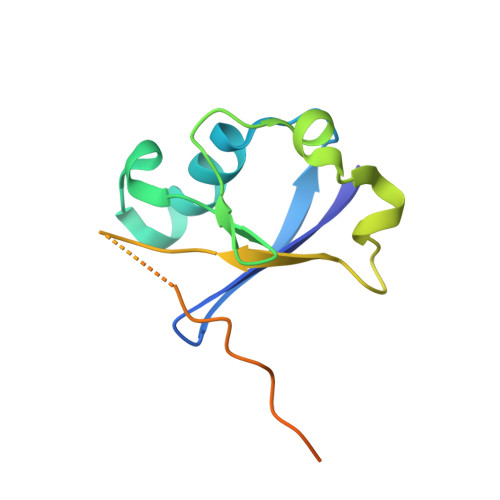
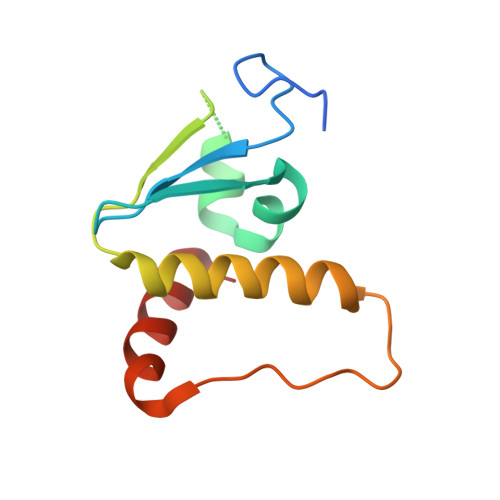
The structural basis for HIV-1 Vif antagonism of human APOBEC3G.
Li, Y.L., Langley, C.A., Azumaya, C.M., Echeverria, I., Chesarino, N.M., Emerman, M., Cheng, Y., Gross, J.D.(2023) Nature 615: 728-733
- PubMed: 36754086
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05779-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8CX0, 8CX1, 8CX2 - PubMed Abstract:
The APOBEC3 (A3) proteins are host antiviral cellular proteins that hypermutate the viral genome of diverse viral families. In retroviruses, this process requires A3 packaging into viral particles 1-4 . The lentiviruses encode a protein, Vif, that antagonizes A3 family members by targeting them for degradation. Diversification of A3 allows host escape from Vif whereas adaptations in Vif enable cross-species transmission of primate lentiviruses. How this 'molecular arms race' plays out at the structural level is unknown. Here, we report the cryogenic electron microscopy structure of human APOBEC3G (A3G) bound to HIV-1 Vif, and the hijacked cellular proteins that promote ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. A small surface explains the molecular arms race, including a cross-species transmission event that led to the birth of HIV-1. Unexpectedly, we find that RNA is a molecular glue for the Vif-A3G interaction, enabling Vif to repress A3G by ubiquitin-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Our results suggest a model in which Vif antagonizes A3G by intercepting it in its most dangerous form for the virus-when bound to RNA and on the pathway to packaging-to prevent viral restriction. By engaging essential surfaces required for restriction, Vif exploits a vulnerability in A3G, suggesting a general mechanism by which RNA binding helps to position key residues necessary for viral antagonism of a host antiviral gene.
- Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: