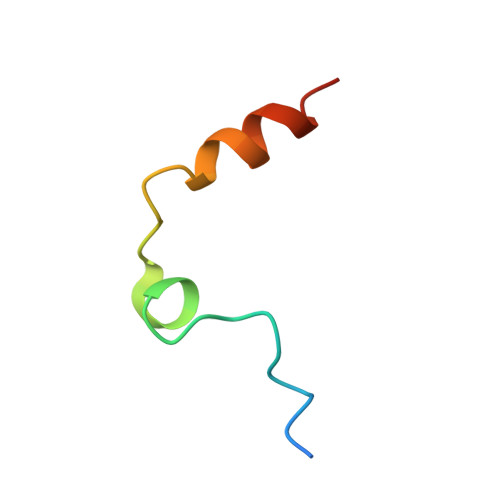
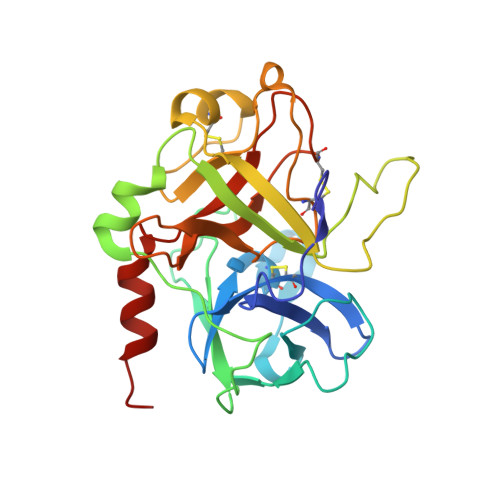
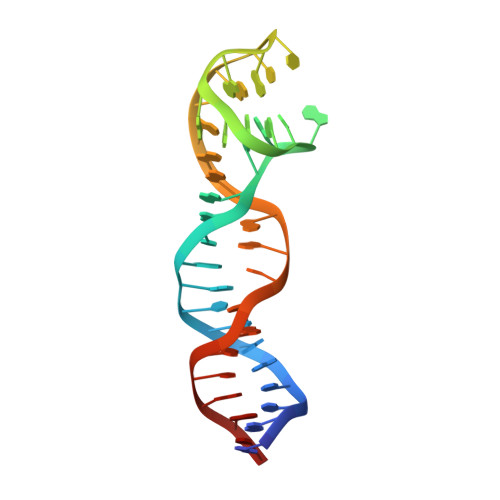
Steric hindrance and structural flexibility shape the functional properties of a guanine-rich oligonucleotide.
Troisi, R., Napolitano, V., Rossitto, E., Osman, W., Nagano, M., Wakui, K., Popowicz, G.M., Yoshimoto, K., Sica, F.(2023) Nucleic Acids Res 51: 8880-8890
- PubMed: 37503836
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad634
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8BW5 - PubMed Abstract:
Ligand/protein molecular recognition involves a dynamic process, whereby both partners require a degree of structural plasticity to regulate the binding/unbinding event. Here, we present the characterization of the interaction between a highly dynamic G-rich oligonucleotide, M08s-1, and its target protein, human α-thrombin. M08s-1 is the most active anticoagulant aptamer selected thus far. Circular dichroism and gel electrophoresis analyses indicate that both intramolecular and intermolecular G-quadruplex structures are populated in solution. The presence of thrombin stabilises the antiparallel intramolecular chair-like G-quadruplex conformation, that provides by far the main contribution to the biological activity of the aptamer. The crystal structure of the thrombin-oligonucleotide complex reveals that M08s-1 adopts a kinked structural organization formed by a G-quadruplex domain and a long duplex module, linked by a stretch of five purine bases. The quadruplex motif hooks the exosite I region of thrombin and the duplex region is folded towards the surface of the protein. This structural feature, which has never been observed in other anti-exosite I aptamers with a shorter duplex motif, hinders the approach of a protein substrate to the active site region and may well explain the significant increase in the anticoagulant activity of M08s-1 compared to the other anti-exosite I aptamers.
- Department of Chemical Sciences, University of Naples Federico II, Naples 80126, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: