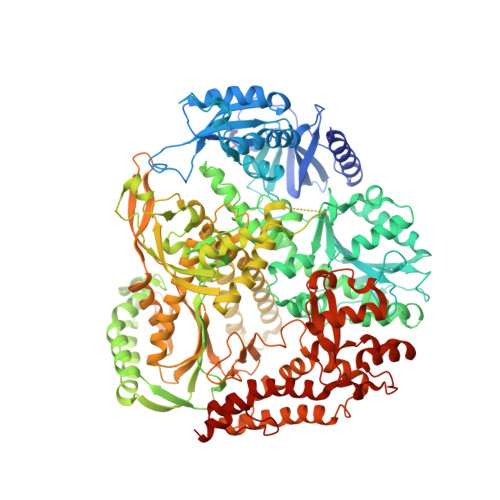
A sensor complements the steric gate when DNA polymerase epsilon discriminates ribonucleotides.
Parkash, V., Kulkarni, Y., Bylund, G.O., Osterman, P., Kamerlin, S.C.L., Johansson, E.(2023) Nucleic Acids Res
- PubMed: 37819038
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad817
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8B67, 8B6K, 8B76, 8B77, 8B79, 8B7E - PubMed Abstract:
The cellular imbalance between high concentrations of ribonucleotides (NTPs) and low concentrations of deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs), is challenging for DNA polymerases when building DNA from dNTPs. It is currently believed that DNA polymerases discriminate against NTPs through a steric gate model involving a clash between a tyrosine and the 2'-hydroxyl of the ribonucleotide in the polymerase active site in B-family DNA polymerases. With the help of crystal structures of a B-family polymerase with a UTP or CTP in the active site, molecular dynamics simulations, biochemical assays and yeast genetics, we have identified a mechanism by which the finger domain of the polymerase sense NTPs in the polymerase active site. In contrast to the previously proposed polar filter, our experiments suggest that the amino acid residue in the finger domain senses ribonucleotides by steric hindrance. Furthermore, our results demonstrate that the steric gate in the palm domain and the sensor in the finger domain are both important when discriminating NTPs. Structural comparisons reveal that the sensor residue is conserved among B-family polymerases and we hypothesize that a sensor in the finger domain should be considered in all types of DNA polymerases.
- Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Umeå University, Umeå 90187, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: