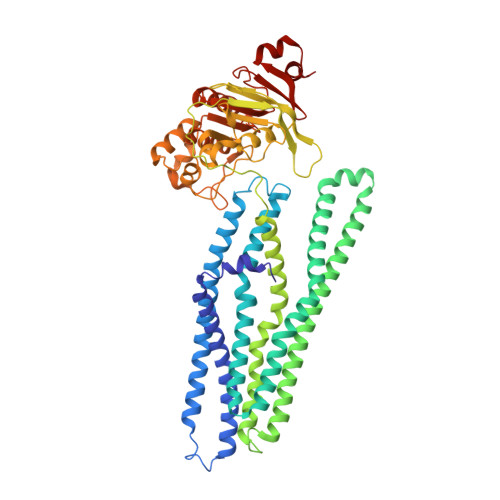
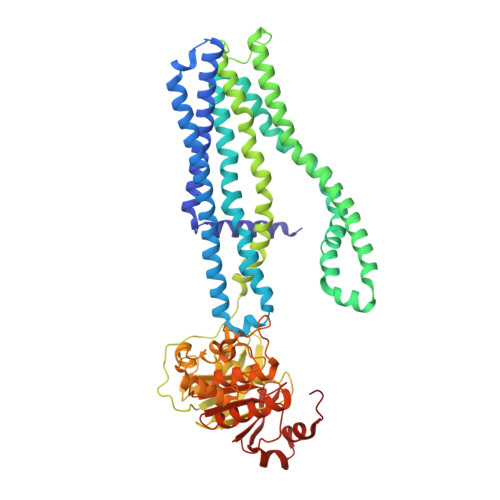
Dissecting the conformational complexity and mechanism of a bacterial heme transporter.
Wu, D., Mehdipour, A.R., Finke, F., Goojani, H.G., Groh, R.R., Grund, T.N., Reichhart, T.M.B., Zimmermann, R., Welsch, S., Bald, D., Shepherd, M., Hummer, G., Safarian, S.(2023) Nat Chem Biol 19: 992-1003
- PubMed: 37095238
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-023-01314-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ZD5, 7ZDA, 7ZDB, 7ZDC, 7ZDE, 7ZDF, 7ZDG, 7ZDK, 7ZDL, 7ZDR, 7ZDS, 7ZDT, 7ZDU, 7ZDV, 7ZDW, 7ZE5, 7ZEC - PubMed Abstract:
Iron-bound cyclic tetrapyrroles (hemes) are redox-active cofactors in bioenergetic enzymes. However, the mechanisms of heme transport and insertion into respiratory chain complexes remain unclear. Here, we used cellular, biochemical, structural and computational methods to characterize the structure and function of the heterodimeric bacterial ABC transporter CydDC. We provide multi-level evidence that CydDC is a heme transporter required for functional maturation of cytochrome bd, a pharmaceutically relevant drug target. Our systematic single-particle cryogenic-electron microscopy approach combined with atomistic molecular dynamics simulations provides detailed insight into the conformational landscape of CydDC during substrate binding and occlusion. Our simulations reveal that heme binds laterally from the membrane space to the transmembrane region of CydDC, enabled by a highly asymmetrical inward-facing CydDC conformation. During the binding process, heme propionates interact with positively charged residues on the surface and later in the substrate-binding pocket of the transporter, causing the heme orientation to rotate 180°.
- Department of Molecular Membrane Biology, Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, Frankfurt/Main, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: