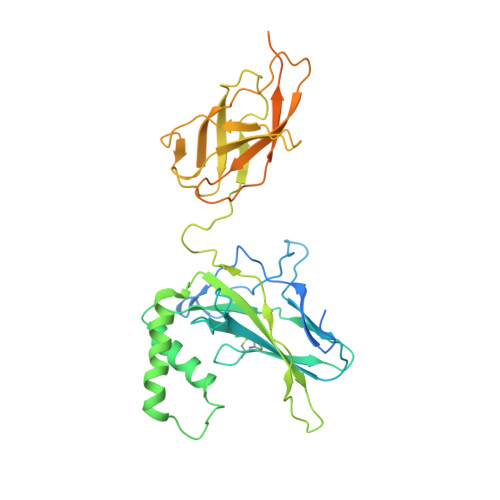
Structures of NF-kappa B p52 homodimer-DNA complexes rationalize binding mechanisms and transcription activation.
Pan, W., Meshcheryakov, V.A., Li, T., Wang, Y., Ghosh, G., Wang, V.Y.(2023) Elife 12
- PubMed: 36779700
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.86258
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7CLI, 7VUP, 7VUQ, 7W7L - PubMed Abstract:
The mammalian NF-κB p52:p52 homodimer together with its cofactor Bcl3 activates transcription of κB sites with a central G/C base pair (bp), while it is inactive toward κB sites with a central A/T bp. To understand the molecular basis for this unique property of p52, we have determined the crystal structures of recombinant human p52 protein in complex with a P-selectin(PSel)-κB DNA (5'-GGGGT G ACCCC-3') (central bp is underlined) and variants changing the central bp to A/T or swapping the flanking bp. The structures reveal a nearly two-fold widened minor groove in the central region of the DNA as compared to all other currently available NF-κB-DNA complex structures, which have a central A/T bp. Microsecond molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of free DNAs and p52 bound complexes reveal that free DNAs exhibit distinct preferred conformations, and p52:p52 homodimer induces the least amount of DNA conformational changes when bound to the more transcriptionally active natural G/C-centric PSel-κB, but adopts closed conformation when bound to the mutant A/T and swap DNAs due to their narrowed minor grooves. Our binding assays further demonstrate that the fast kinetics favored by entropy is correlated with higher transcriptional activity. Overall, our studies have revealed a novel conformation for κB DNA in complex with NF-κB and pinpoint the importance of binding kinetics, dictated by DNA conformational and dynamic states, in controlling transcriptional activation for NF-κB.
- Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Taipa, China.
Organizational Affiliation: