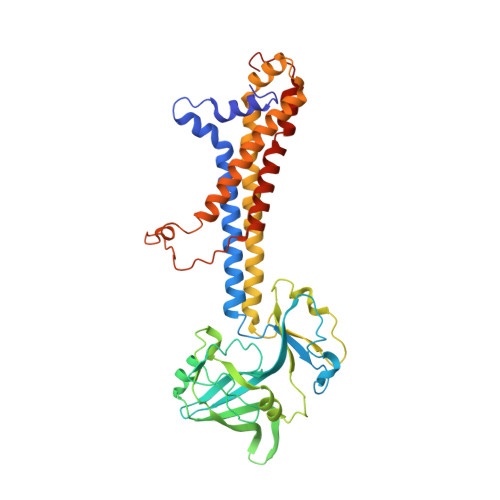
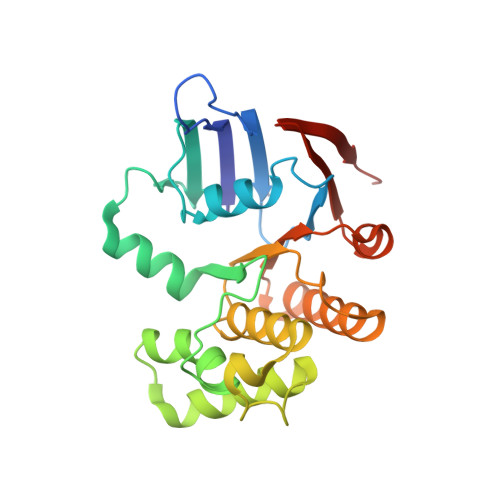
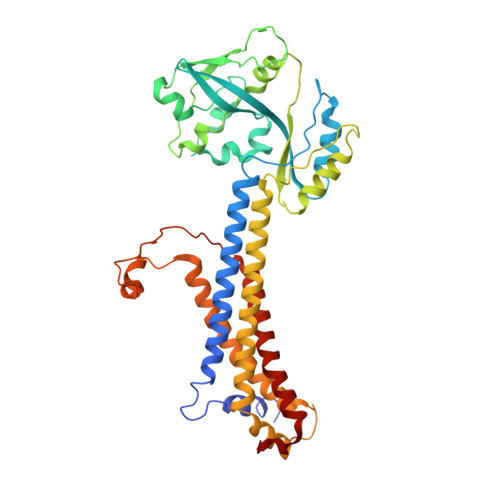
Cryo-EM structures of LolCDE reveal the molecular mechanism of bacterial lipoprotein sorting in Escherichia coli.
Bei, W., Luo, Q., Shi, H., Zhou, H., Zhou, M., Zhang, X., Huang, Y.(2022) PLoS Biol 20: e3001823-e3001823
- PubMed: 36228045
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001823
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7V8I, 7V8L, 7V8M - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial lipoproteins perform a diverse array of functions including bacterial envelope biogenesis and microbe-host interactions. Lipoproteins in gram-negative bacteria are sorted to the outer membrane (OM) via the localization of lipoproteins (Lol) export pathway. The ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter LolCDE initiates the Lol pathway by selectively extracting and transporting lipoproteins for trafficking. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of LolCDE in apo, lipoprotein-bound, and AMPPNP-bound states at a resolution of 3.5 to 4.2 Å. Structure-based disulfide crosslinking, photo-crosslinking, and functional complementation assay verify the apo-state structure and reveal the molecular details regarding substrate selectivity and substrate entry route. Our studies snapshot 3 functional states of LolCDE in a transport cycle, providing deep insights into the mechanisms that underlie LolCDE-mediated lipoprotein sorting in E. coli.
- National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
Organizational Affiliation: