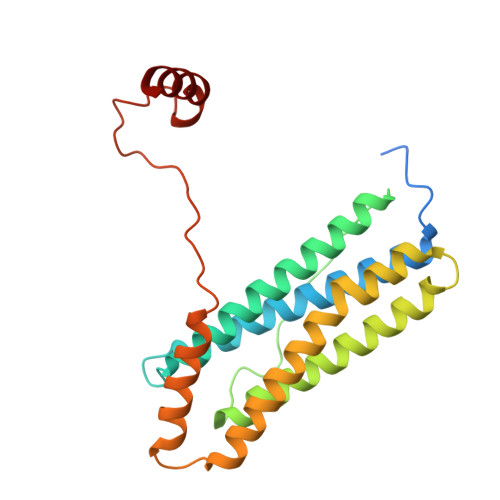
Cryo-EM structure of the diapause chaperone artemin.
Parvate, A.D., Powell, S.M., Brookreson, J.T., Moser, T.H., Novikova, I.V., Zhou, M., Evans, J.E.(2022) Front Mol Biosci 9: 998562-998562
- PubMed: 36518848
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.998562
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7RVB - PubMed Abstract:
The protein artemin acts as both an RNA and protein chaperone and constitutes over 10% of all protein in Artemia cysts during diapause. However, its mechanistic details remain elusive since no high-resolution structure of artemin exists. Here we report the full-length structure of artemin at 2.04 Å resolution. The cryo-EM map contains density for an intramolecular disulfide bond between Cys22-Cys61 and resolves the entire C-terminus extending into the core of the assembled protein cage but in a different configuration than previously hypothesized with molecular modeling. We also provide data supporting the role of C-terminal helix F towards stabilizing the dimer form that is believed to be important for its chaperoning activity. We were able to destabilize this effect by placing a tag at the C-terminus to fully pack the internal cavity and cause limited steric hindrance.
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, Richland, WA, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: