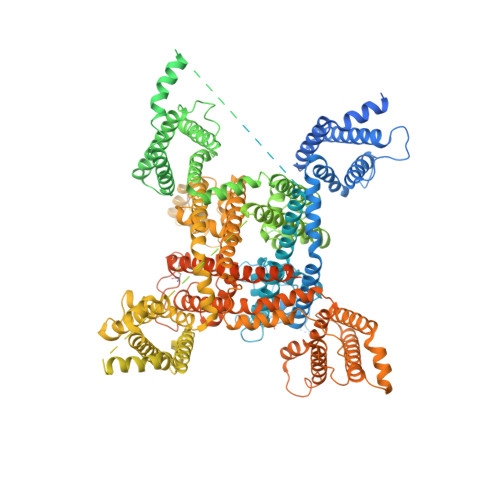
Comparative structural analysis of human Na v 1.1 and Na v 1.5 reveals mutational hotspots for sodium channelopathies.
Pan, X., Li, Z., Jin, X., Zhao, Y., Huang, G., Huang, X., Shen, Z., Cao, Y., Dong, M., Lei, J., Yan, N.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 33712547
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2100066118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DTD - PubMed Abstract:
Among the nine subtypes of human voltage-gated sodium (Na v ) channels, the brain and cardiac isoforms, Na v 1.1 and Na v 1.5, each carry more than 400 missense mutations respectively associated with epilepsy and cardiac disorders. High-resolution structures are required for structure-function relationship dissection of the disease variants. We report the cryo-EM structures of the full-length human Na v 1.1-β4 complex at 3.3 Å resolution here and the Na v 1.5-E1784K variant in the accompanying paper. Up to 341 and 261 disease-related missense mutations in Na v 1.1 and Na v 1.5, respectively, are resolved. Comparative structural analysis reveals several clusters of disease mutations that are common to both Na v 1.1 and Na v 1.5. Among these, the majority of mutations on the extracellular loops above the pore domain and the supporting segments for the selectivity filter may impair structural integrity, while those on the pore domain and the voltage-sensing domains mostly interfere with electromechanical coupling and fast inactivation. Our systematic structural delineation of these mutations provides important insight into their pathogenic mechanism, which will facilitate the development of precise therapeutic interventions against various sodium channelopathies.
- State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China; panxj@tsinghua.edu.cn nyan@princeton.edu.
Organizational Affiliation: