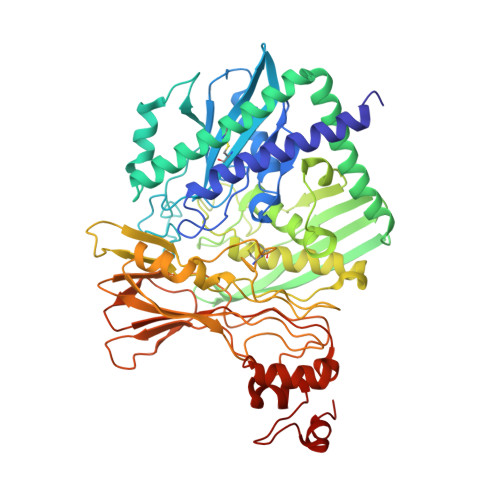
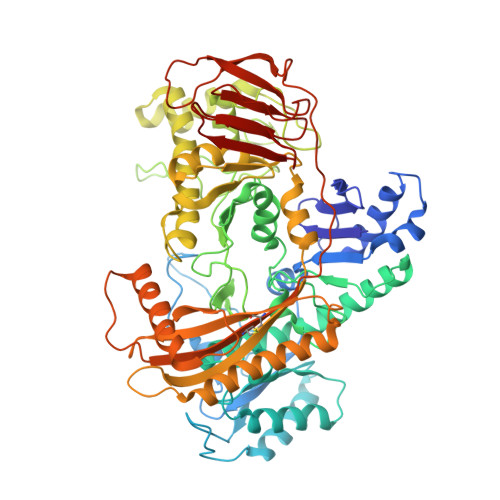
Catalytic and structural properties of ATP-dependent caprolactamase from Pseudomonas jessenii.
Marjanovic, A., Rozeboom, H.J., de Vries, M.S., Mayer, C., Otzen, M., Wijma, H.J., Janssen, D.B.(2021) Proteins 89: 1079-1098
- PubMed: 33826169
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.26082
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6YRA - PubMed Abstract:
Caprolactamase is the first enzyme in the caprolactam degradation pathway of Pseudomonas jessenii. It is composed of two subunits (CapA and CapB) and sequence-related to other ATP-dependent enzymes involved in lactam hydrolysis, like 5-oxoprolinases and hydantoinases. Low sequence similarity also exists with ATP-dependent acetone- and acetophenone carboxylases. The caprolactamase was produced in Escherichia coli, isolated by His-tag affinity chromatography, and subjected to functional and structural studies. Activity toward caprolactam required ATP and was dependent on the presence of bicarbonate in the assay buffer. The hydrolysis product was identified as 6-aminocaproic acid. Quantum mechanical modeling indicated that the hydrolysis of caprolactam was highly disfavored (ΔG 0 '= 23 kJ/mol), which explained the ATP dependence. A crystal structure showed that the enzyme exists as an (αβ) 2 tetramer and revealed an ATP-binding site in CapA and a Zn-coordinating site in CapB. Mutations in the ATP-binding site of CapA (D11A and D295A) significantly reduced product formation. Mutants with substitutions in the metal binding site of CapB (D41A, H99A, D101A, and H124A) were inactive and less thermostable than the wild-type enzyme. These residues proved to be essential for activity and on basis of the experimental findings we propose possible mechanisms for ATP-dependent lactam hydrolysis.
- Biotransformation and Biocatalysis, Groningen Biomolecular Sciences and Biotechnology Institute (GBB), University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands.
Organizational Affiliation: