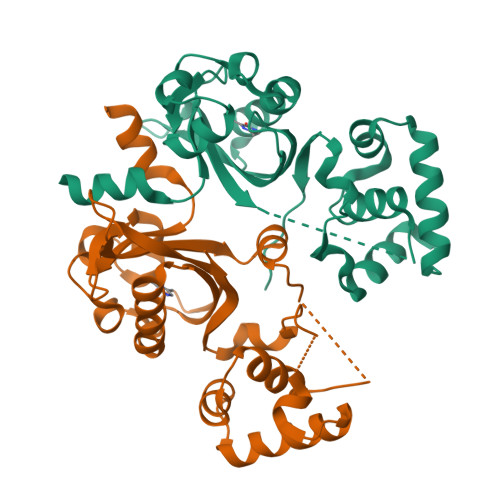
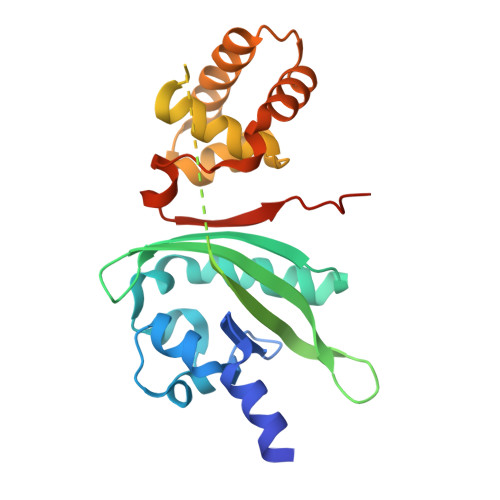
Mechanism underlying autoinducer recognition in theVibrio choleraeDPO-VqmA quorum-sensing pathway.
Huang, X., Duddy, O.P., Silpe, J.E., Paczkowski, J.E., Cong, J., Henke, B.R., Bassler, B.L.(2020) J Biological Chem 295: 2916-2931
- PubMed: 31964715
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.012104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6UGL - PubMed Abstract:
Quorum sensing is a bacterial communication process whereby bacteria produce, release, and detect extracellular signaling molecules called autoinducers to coordinate collective behaviors. In the pathogen Vibrio cholerae , the quorum-sensing autoinducer 3,5-dimethyl-pyrazin-2-ol (DPO) binds the receptor and transcription factor VqmA. The DPO-VqmA complex activates transcription of vqmR , encoding the VqmR small RNA, which represses genes required for biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Here, we show that VqmA is soluble and properly folded and activates basal-level transcription of its target vqmR in the absence of DPO. VqmA transcriptional activity is increased in response to increasing concentrations of DPO, allowing VqmA to drive the V. cholerae quorum-sensing transition at high cell densities. We solved the DPO-VqmA crystal structure to 2.0 Å resolution and compared it with existing structures to understand the conformational changes VqmA undergoes upon DNA binding. Analysis of DPO analogs showed that a hydroxyl or carbonyl group at the 2'-position is critical for binding to VqmA. The proposed DPO precursor, a linear molecule, N -alanyl-aminoacetone (Ala-AA), also bound and activated VqmA. Results from site-directed mutagenesis and competitive ligand-binding analyses revealed that DPO and Ala-AA occupy the same binding site. In summary, our structure-function analysis identifies key features required for VqmA activation and DNA binding and establishes that, whereas VqmA binds two different ligands, VqmA does not require a bound ligand for folding or basal transcriptional activity. However, bound ligand is required for maximal activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey 08544; Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Chevy Chase, Maryland 20815.