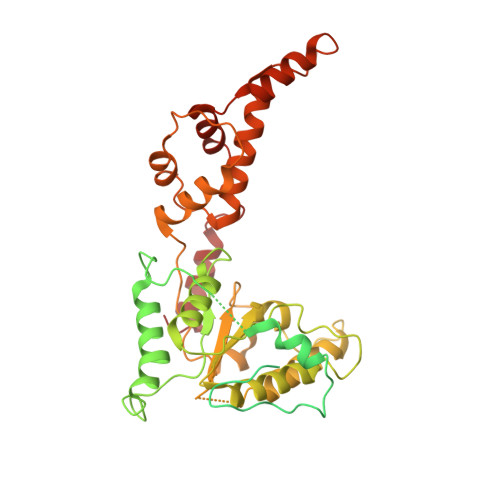
Katanin Grips the beta-Tubulin Tail through an Electropositive Double Spiral to Sever Microtubules.
Zehr, E.A., Szyk, A., Szczesna, E., Roll-Mecak, A.(2020) Dev Cell 52: 118-131.e6
- PubMed: 31735665
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6UGD, 6UGE, 6UGF - PubMed Abstract:
The AAA ATPase katanin severs microtubules. It is critical in cell division, centriole biogenesis, and neuronal morphogenesis. Its mutation causes microcephaly. The microtubule templates katanin hexamerization and activates its ATPase. The structural basis for these activities and how they lead to severing is unknown. Here, we show that β-tubulin tails are necessary and sufficient for severing. Cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures reveal the essential tubulin tail glutamates gripped by a double spiral of electropositive loops lining the katanin central pore. Each spiral couples allosterically to the ATPase and binds alternating, successive substrate residues, with consecutive residues coordinated by adjacent protomers. This tightly couples tail binding, hexamerization, and ATPase activation. Hexamer structures in different states suggest an ATPase-driven, ratchet-like translocation of the tubulin tail through the pore. A disordered region outside the AAA core anchors katanin to the microtubule while the AAA motor exerts the forces that extract tubulin dimers and sever the microtubule.
- Cell Biology and Biophysics Unit, Porter Neuroscience Research Center, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, Bethesda, MD 20982, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: