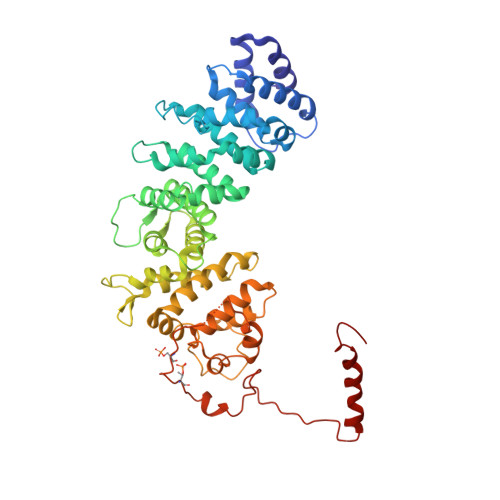
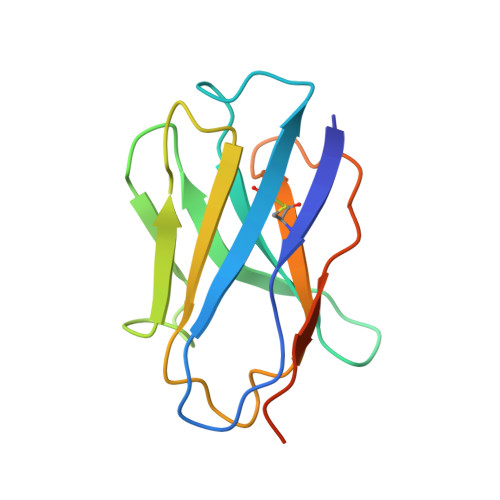
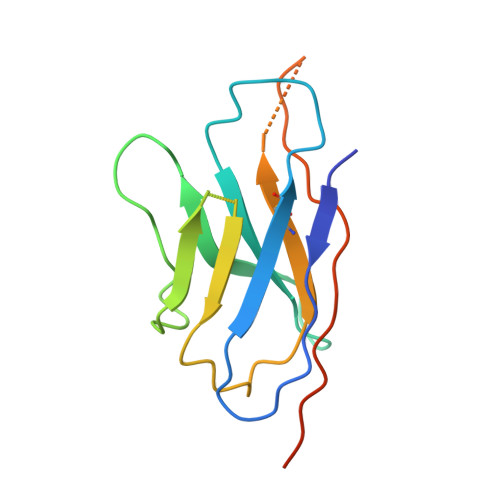
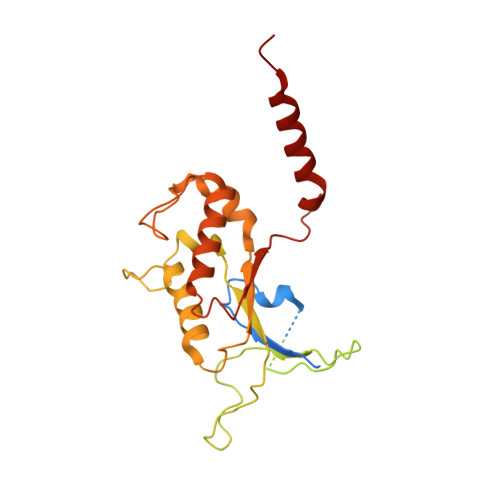
Structure of the G protein chaperone and guanine nucleotide exchange factor Ric-8A bound to G alpha i1.
McClelland, L.J., Zhang, K., Mou, T.C., Johnston, J., Yates-Hansen, C., Li, S., Thomas, C.J., Doukov, T.I., Triest, S., Wohlkonig, A., Tall, G.G., Steyaert, J., Chiu, W., Sprang, S.R.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 1077-1077
- PubMed: 32103024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14943-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TYL, 6UKT - PubMed Abstract:
Ric-8A is a cytosolic Guanine Nucleotide exchange Factor (GEF) that activates heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits (Gα) and serves as an essential Gα chaperone. Mechanisms by which Ric-8A catalyzes these activities, which are stimulated by Casein Kinase II phosphorylation, are unknown. We report the structure of the nanobody-stabilized complex of nucleotide-free Gα bound to phosphorylated Ric-8A at near atomic resolution by cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. The mechanism of Ric-8A GEF activity differs considerably from that employed by G protein-coupled receptors at the plasma membrane. Ric-8A engages a specific conformation of Gα at multiple interfaces to form a complex that is stabilized by phosphorylation within a Ric-8A segment that connects two Gα binding sites. The C-terminus of Gα is ejected from its beta sheet core, thereby dismantling the GDP binding site. Ric-8A binds to the exposed Gα beta sheet and switch II to stabilize the nucleotide-free state of Gα.
- Center for Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, University of Montana, Missoula, MT, 59812, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: