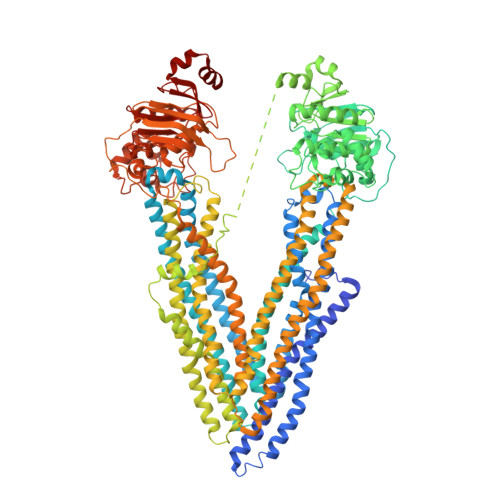
Novel features in the structure of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) in the post-hydrolytic state as determined at 7.9 angstrom resolution.
Thonghin, N., Collins, R.F., Barbieri, A., Shafi, T., Siebert, A., Ford, R.C.(2018) BMC Struct Biol 18: 17-17
- PubMed: 30545335
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12900-018-0098-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6GDI, 6Q81 - PubMed Abstract:
P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) is an ATP-binding cassette transporter that plays an important role in the clearance of drugs and xenobiotics and is associated with multi-drug resistance in cancer. Although several P-glycoprotein structures are available, these are either at low resolution, or represent mutated and/or quiescent states of the protein. In the post-hydrolytic state the structure of the wild-type protein has been resolved at about 8 Å resolution. The cytosolic nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) are separated but ADP remains bound, especially at the first NBD. Gaps in the transmembrane domains (TMDs) that connect to an inner hydrophilic cavity are filled by density emerging from the annular detergent micelle. The NBD-TMD linker is partly resolved, being located between the NBDs and close to the Signature regions involved in cooperative NBD dimerization. This, and the gap-filling detergent suggest steric impediment to NBD dimerization in the post-hydrolytic state. Two central regions of density lie in two predicted drug-binding sites, implying that the protein may adventitiously bind hydrophobic substances even in the post-hydrolytic state. The previously unresolved N-terminal extension was observed, and the data suggests these 30 residues interact with the headgroup region of the lipid bilayer. The structural data imply that (i) a low basal ATPase activity is ensured by steric blockers of NBD dimerization and (ii) allocrite access to the central cavity may be structurally linked to NBD dimerization, giving insights into the mechanism of drug-stimulation of P-glycoprotein activity.
- School of Biology, Faculty of Biology Medicine and Health, Michael Smith Building, The University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester, M13 9PL, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: