Multicomponent Synthesis, Binding Mode, and Structure-Activity Relationship of Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Inhibitors with Bifurcated Capping Groups.
Ressing, N., Sonnichsen, M., Osko, J.D., Scholer, A., Schliehe-Diecks, J., Skerhut, A., Borkhardt, A., Hauer, J., Kassack, M.U., Christianson, D.W., Bhatia, S., Hansen, F.K.(2020) J Med Chem 63: 10339-10351
- PubMed: 32803970
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01888
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PYE - PubMed Abstract:
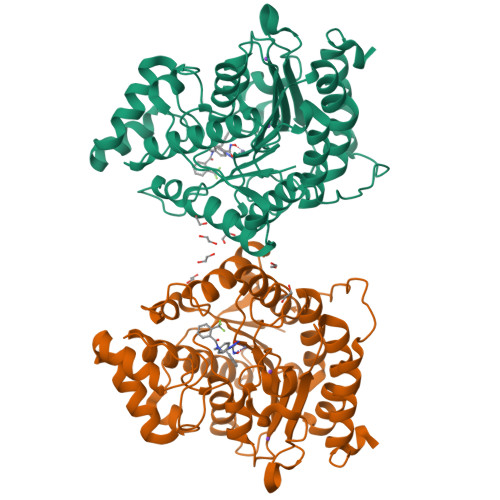
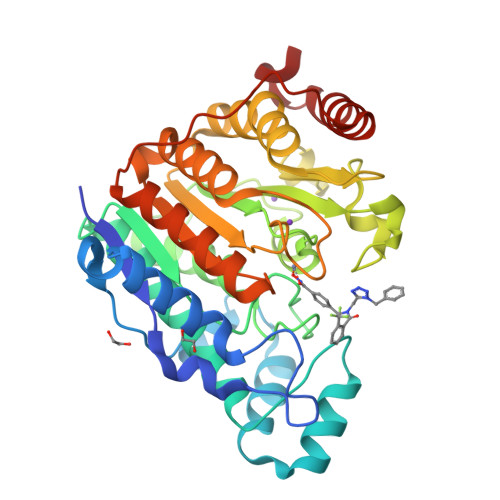
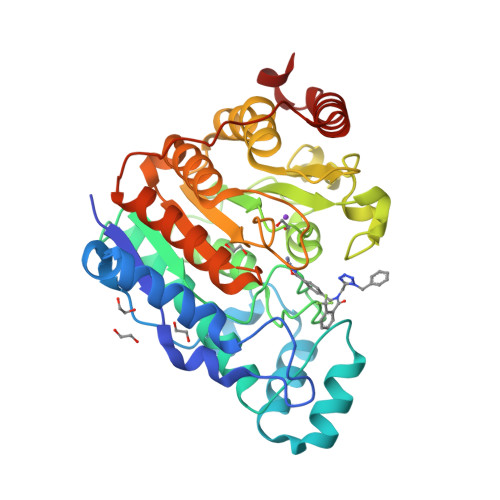
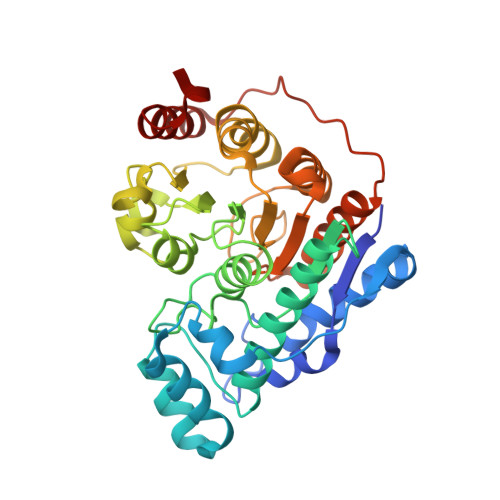
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is an emerging target for the treatment of cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, inflammation, and other diseases. Here, we present the multicomponent synthesis and structure-activity relationship of a series of tetrazole-based HDAC6 inhibitors. We discovered the hit compound NR-160 by investigating the inhibition of recombinant HDAC enzymes and protein acetylation. A cocrystal structure of HDAC6 complexed with NR-160 disclosed that the steric complementarity of the bifurcated capping group of NR-160 to the L1 and L2 loop pockets may be responsible for its HDAC6-selective inhibition. While NR-160 displayed only low cytotoxicity as a single agent against leukemia cell lines, it augmented the apoptosis induction of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in combination experiments significantly. Furthermore, a combinatorial high-throughput drug screen revealed significantly enhanced cytotoxicity when NR-160 was used in combination with epirubicin and daunorubicin. The synergistic effect in combination with bortezomib and anthracyclines highlights the potential of NR-160 in combination therapies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Drug Discovery, Medical Faculty, Leipzig University, Brüderstr. 34, 04103 Leipzig, Germany.