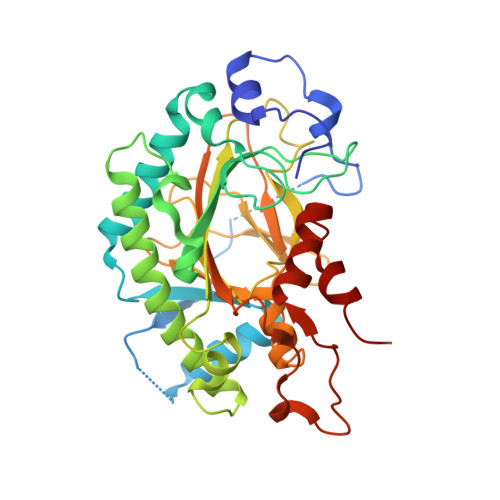
Structure-guided analysis of Arabidopsis JASMONATE-INDUCED OXYGENASE (JOX) 2 reveals key residues for recognition of jasmonic acid substrate by plant JOXs.
Zhang, X., Wang, D., Elberse, J., Qi, L., Shi, W., Peng, Y.L., Schuurink, R.C., Van den Ackerveken, G., Liu, J.(2021) Mol Plant 14: 820-828
- PubMed: 33516967
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.01.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LSV - PubMed Abstract:
The jasmonic acid (JA) signaling pathway is used by plants to control wound responses. The persistent accumulation of JA inhibits plant growth, and the hydroxylation of JA to 12-hydroxy-JA by JASMONATE-INDUCED OXYGENASEs (JOXs, also named jasmonic acid oxidases) is therefore vital for plant growth, while structural details of JA recognition by JOXs are unknown. Here, we present the 2.65 Å resolution X-ray crystal structure of Arabidopsis JOX2 in complex with its substrate JA and its co-substrates 2-oxoglutarate and Fe(II). JOX2 contains a distorted double-stranded β helix (DSBH) core flanked by α helices and loops. JA is bound in the narrow substrate pocket by hydrogen bonds with the arginine triad R225, R350, and R354 and by hydrophobic interactions mainly with the phenylalanine triad F157, F317, and F346. The most critical residues for JA binding are F157 and R225, both from the DSBH core, which interact with the cyclopentane ring of JA. The spatial distribution of critical residues for JA binding and the shape of the substrate-binding pocket together define the substrate selectivity of the JOXs. Sequence alignment shows that these critical residues are conserved among JOXs from higher plants. Collectively, our study provides insights into the mechanism by which higher plants hydroxylate the hormone JA.
- State Key Laboratory of Agrobiotechnology, Ministry of Agriculture Key Laboratory for Crop Pest Monitoring and Green Control, Joint International Research Laboratory of Crop Molecular Breeding, College of Plant Protection, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China.
Organizational Affiliation: