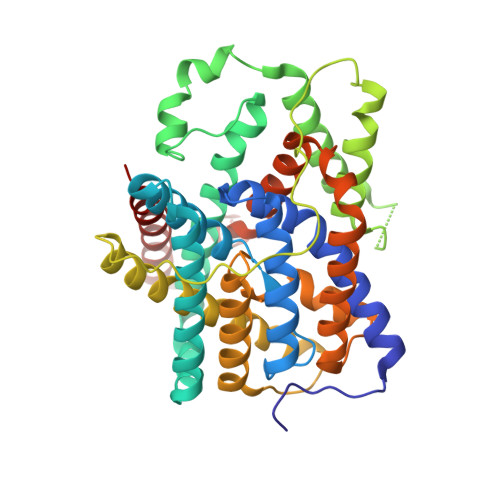
Structural mechanism of the active bicarbonate transporter from cyanobacteria.
Wang, C., Sun, B., Zhang, X., Huang, X., Zhang, M., Guo, H., Chen, X., Huang, F., Chen, T., Mi, H., Yu, F., Liu, L.N., Zhang, P.(2019) Nat Plants 5: 1184-1193
- PubMed: 31712753
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-019-0538-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6KI1, 6KI2 - PubMed Abstract:
Bicarbonate transporters play essential roles in pH homeostasis in mammals and photosynthesis in aquatic photoautotrophs. A number of bicarbonate transporters have been characterized, among which is BicA-a low-affinity, high-flux SLC26-family bicarbonate transporter involved in cyanobacterial CO 2 -concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) that accumulate CO 2 and improve photosynthetic carbon fixation. Here, we report the three-dimensional structure of BicA from Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Crystal structures of the transmembrane domain (BicA TM ) and the cytoplasmic STAS domain (BicA STAS ) of BicA were solved. BicA TM was captured in an inward-facing HCO 3 - -bound conformation and adopts a '7+7' fold monomer. HCO 3 - binds to a cytoplasm-facing hydrophilic pocket within the membrane. BicA STAS is assembled as a compact homodimer structure and is required for the dimerization of BicA. The dimeric structure of BicA was further analysed using cryo-electron microscopy and physiological analysis of the full-length BicA, and may represent the physiological unit of SLC26-family transporters. Comparing the BicA TM structure with the outward-facing transmembrane domain structures of other bicarbonate transporters suggests an elevator transport mechanism that is applicable to the SLC26/4 family of sodium-dependent bicarbonate transporters. This study advances our knowledge of the structures and functions of cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporters, and will inform strategies for bioengineering functional BicA in heterologous organisms to increase assimilation of CO 2 .
- National Key Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: