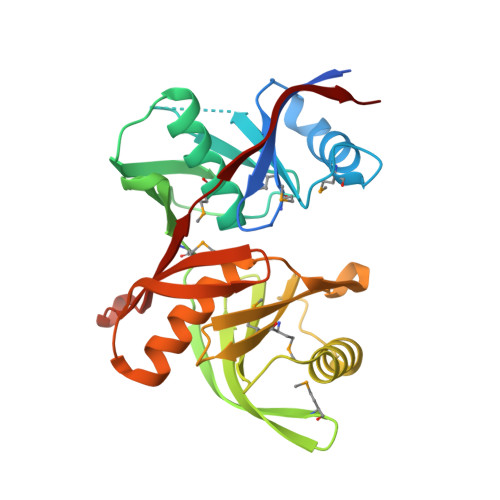
Crystal structure of CntK, the cofactor-independent histidine racemase in staphylopine-mediated metal acquisition of Staphylococcus aureus.
Luo, S., Ju, Y., Zhou, J., Gu, Q., Xu, J., Zhou, H.(2019) Int J Biol Macromol 135: 725-733
- PubMed: 31129210
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.169
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JIS, 6JIW - PubMed Abstract:
Staphylopine is a newly identified broad-spectrum metallophore for metal acquisition, and it plays important roles in the survival and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus and other pathogens in the metal-scarce environment in hosts. CntK catalyzes the first step of staphylopine synthesis by converting L-histidine to D-histidine to provide an essential building block of staphylopine. Herein, the crystal structures of S. aureus CntK (SaCntK) and its C72S variant are determined at 1.82 and 1.58 Å resolution, respectively. SaCntK forms a homodimer and each subunit contains a two-domain α/β structure. Its overall structure resembles diaminopimelate epimerase, although their sequence identities are lower than 22%. SaCntK is specific for histidine, whereas other proteinogenic amino acids, with the exception of arginine, do not show any binding with SaCntK. Structural modeling suggested that residues Asn16, Glu46, Gln47 and Glu208 are responsible for specific substrate binding, and their substitutions significantly reduced the binding of histidine to SaCntK. Structural modeling suggested SaCntK uses a two-base catalytic mechanism, which has been observed in many cofactor-independent racemases. Our study provides critical insights into the structure and functions of CntK in staphylopine synthesis, which makes it helpful for developing potential antibiotics targeting the staphylopine-mediated metal acquisition process in bacteria.
- Guangdong Key Laboratory of Chiral Molecule and Drug Discovery, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
Organizational Affiliation: